Файлы
Раздел содержит файлы для скачивания по теме вилочных погрузчиков.
Инструкции по эксплуатации |
Инструкции по эксплуатации вилочных погрузчиковДоступны для скачивания инструкции и руководства для погрузчиков: Komatsu, Toyota, Yale. Все инструкции для вилочных погрузчиков содержат следующую информацию:
Руководство оператора штабелераДоступно для скачивания руководство оператора для штабелера BT. Кроме стандартной информации инструкция содержит цифровые коды предупреждений и ошибок. |
|
Руководство оператора штабелера BT SPE125 SPE160 |
| Правила техники безопасности Описание штабелера Технические данные Основные узлы и детали Органы управления Цифровые коды ошибок Вождение Перемещение грузов Аккумуляторная батарея Техобслуживание батареи График проведения планового техобслуживания Таблица смазки различных узлов и деталей |
|
Дата: 2015-01-07 18:06:12 Размер: 2.3 Мб Скачано: 17264 |
| Вернуться |
| Список категорий |
Toyota Forklift Error Codes List pdf Download
Toyota Forklift 8FD/FG series Error Codes Download
Toyota Forklift fault (error) codes — List Of Diagnosis Codes 1 Download
Toyota Forklift fault (error) codes — List Of Diagnosis Codes 2 Download
Toyota Forklift fault (error) codes — List Of Diagnosis Codes 3 Download
Toyota Forklift fault (error) codes — List Of Diagnosis Codes 4 Download
Toyota Forklift fault (error) codes — List Of Diagnosis Codes 5 Download
Toyota Forklift fault (error) codes — List Of Diagnosis Codes 6 Download
MODEL APPLICATION:
7FBCU15, 7FBCU18, 7FBCU20, 7FBCU25, 7FBCU30, 7FBCU32 7FBCU35, 7FBCU45, 7FBCU55, 7FBCHU18, 7FBCHU25 7FBEU15, 7FBEU18, 7FBEU20, 7FBEHU18, 7FGU15, 7FGU18 7FGU20, 7FGU25, 7FGU30, 7FGU32, 7FDU15,
7FDU18, 7FDU20 7FDU25, 7FDU30, 7FDU32, 8FGU15, 8FGU18, 8FGU20, 8FGU25 8FGU30, 8FGU32, 8FDU15, 8FDU18, 8FDU20, 8FDU25, 8FDU30 8FDU32, 7FGCU15, 7FGCU18, 7FGCU20, 7FGCSU20, 7FGCU25 7FGCU30, 7FGCU32,
8FGCU18, 8FGCU20, 8FGCSU20, 8FGCU25 8FGCU30, 8FGCU32, 7FGU35, 7FDU35, 7FGKU40, 7FDKU40 7FGU45, 7FDU45, 7FGAU50, 7FDAU50, 7FGU60, 7FDU60, 7FGU70 7FDU70, 7FGU80, 7FDU80, 7FGCU35, 7FGCU45, 7FGCU55
7FGCU60, 7FGCU70
GENERAL INFORMATION:
All three error codes are for the same condition. • A5 is for sit-down electric trucks (Class I) • A5-1 is for 8-Series internal combustion trucks (Class IV & V) • 1-1 is for 7-Series
internal combustion trucks (Class IV & V) with OPSS (Operator Presence Sensing System)
Further information concerning these codes can be found in the following manuals:
7FBCU15-55 ►OPSS Manual CU335 page 3-9 7FBEU15-20 ►OPSS Manual CU341 page 1-10 7FGCU15, 18, S20 ►OPSS Manual CU042 page 1-19 7FGU15-32, 7FDU15-32, 7FGCU20-32 ►OPSS Manual CU040 page 1-18
7FGU35-80, 7FDU35-80, 7FGCU35-70 ►OPSS Manual CU041 page 1-17 8FGCU15, 18, S20 ►Service manual 00700-X8880-71 page 19.1-82 8FGU15-32, 8FDU15-32, 8FGCU20-32 ►Service manual 00700-X8880-71 page
19-111
DIAGNOSIS DISPLAY METHOD
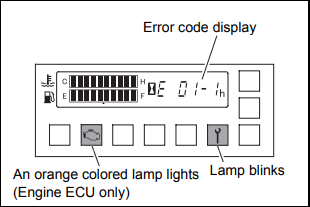
1. Diagnosis display method The diagnosis is displayed by means of an error code as shown in the illustration to the left, and by the lights turning on. When the ignition key switch is turned ON,
the lamp lights once to allow checking for the bulb, and then turns off again if the status is normal. With the ignition key switch ON, if an abnormality is detected when the vehicle is stopped,
travelling or performing meterials handling operations, an error code is displayed and the lamps turn on as a warning. When this happens, stop the vehicle immediately and check the error code.
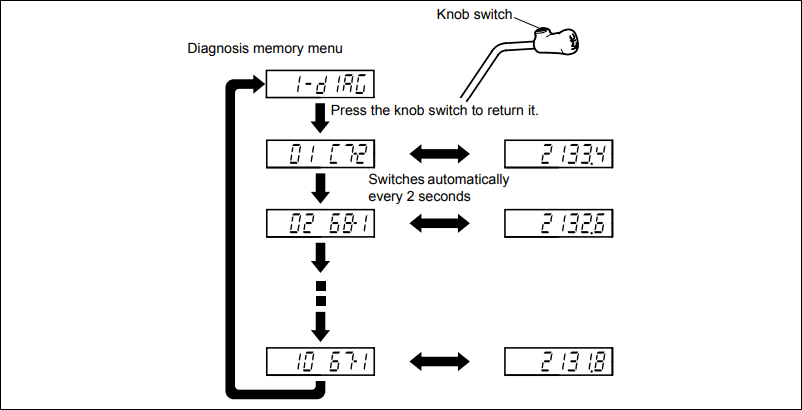
2. Diagnosis memory display method To display the diagnosis memory display, there are a method using the hour meter and tilt lever, a method using the optional display, and a method using a
plug-in analyzer. Here the display method using the hour meter and tilt lever is described. (1) From the main menu, display the diagnosis memory menu. For how to display the main menu, refer to
page 18-30. (2) A diagnosis No. and error code are displayed each time the knob switch is pressed and released. Each error code and the time at which it occurred are displayed alternately at 2
second intervals.
(3) Connect the matching connector and turn the ignition key switch OFF.
LIST OF DIAGNOSIS CODES

Translated from Indonesian!
Original text error codes Download
41-1 Matching connector abnormal Only the Connector display is faulty
Matching cable is broken
Controller is broken
51-1 Speed sensor abnormal Speed indicator keeps showing 0 km/h Connector is faulty
51-2 Rear wheel swing control Damaged connector cable
Steer knob is not in position Speed sensor is broken
Controller is broken
52-1 Yaw rate sensor abnormal Rear wheel swing control is limited. Broken connector
52-2 Connector cable is damaged
52-3 Yaw rate sensor is faulty
Controller is broken
54-1 Swing lock solenoid abnormal Rear wheel swing control is limited. Broken connector
Broken connector cable
Swing lock solenoid is broken
Controller is broken
61-1 Load sensor abnormal Rear wheel swing control is limited. Broken connector
61-2 Control mast function is partially restricted Connector cable is damaged
Drive control function is limited (MFD opt) Load sensor is faulty
Load indicator does not appear on the display (MFD) The controller is broken
Error mode Symptoms on forklift Possible causes
damaged
62-1 Tilt angle sensor abnormal Mast control function is partially restricted Connector is faulty
62-2 Connector cable is damaged
Broken tilt angle sensor
Controller is broken
63-1 Tilt lever switch abnormal Mast control function is partially restricted Connector is faulty
63-2 Forward tilt switch is broken
63-3 Backward tilt switch is broken
Broken cable
Faulty switch installation
Controller is broken
64-1 Lift lock solenoid abnormal Fork won’t come down Connector is broken
Broken connector cable
Broken lift lock solenoid
Controller is broken
65-1 Tilt control solenoid abnormal Forward tilt cannot operate, but Connector is damaged
backward tilt operable. Broken connector cable
Broken tilt control solenoid
Controller is broken
66-1 Abnormal matching measurement value The control mast function is partially restricted. The horizontal tilt angle value does not match.
Tilt forward angle value
it is not in accordance with.
Measuring value of load sensor
it is not in accordance with.
67-1 Lifting height switch abnormal Partial rearwheel swing control function Faulty connector
restricted. Broken connector cable
Mast control function is partially restricted Lifting height swt is broken
Drive control function is restricted Controller is faulty
Load indicator display changes IG fuse blown
68-1 Lift switch abnormal Fork won’t come down Connector is broken
68-2 Raising lift swt is broken
68-3 Lowering lift swt is broken
Broken connector cable
The swt elevator installation is broken
Controller is broken
Error mode Symptoms on the forklift Possible cause of failure
69-1 Backward tilt lock solenoid Backward tilt does not operate Connector is faulty
abnormal Connector cable is damaged
Backward tilt lock solenoid is faulty.
Controller is broken
71-1 Tire angle sensor abnormal Steer knob is not in position Connector is faulty
71-2 Connector cable is damaged
Broken sensor
tire angle sensor joint,
rear axle link syst. damaged
Controller is broken
72-1 Steering angle sensor abnormal Steer knob is not in position Connector is faulty
72-2 Connector cable is damaged
72-3 Sensor is faulty
72-4 Controller is faulty
73-1 Abnormal solenoid knob position Steer knob out of position Connector is faulty
Broken connector cable
Broken solenoid
Controller is broken
74-1 Measuring value of matching tire angle Steer knob is not in position Matching value
wheel alignment error no in accordance
A5-1 Seat switch abnormal Drive & hydraulic system can operate Connector is faulty
even if the operator is not sitting in the operating chair The connector cable is damaged
Broken switch
Controller is broken
A7-1 Abnormal brake switch Function of partially restricted drive control Connector is faulty
Broken brake switch
Broken connector cable
Controller is broken
AF-1
AF-2
AF-3
AF-4
AF-5
AF-6
AF-7
AF-8 CPU abnormal All control functions are unstable Controller is faulty
C7-1 Shift lever switch abnormal Cannot be positioned to neutral Connector is faulty
C7-2 Drive control function is partially restricted Forward switch is faulty
Reverse switch is broken
Broken cable
Faulty switch installation
Controller is broken
CA-1 Forward-reverse travel Torque Drive system and hydraulic system can Connector damaged
converter relay abnormal is operated even when operator is not seated Forward travel cable
the relay operator seat is broken
Forward travel relay
damaged
reverse travel cable
broken relay
Reverse travel relay
damaged
Controller is broken
EC-1 Unload solenoid abnormal Drive system and hydraulic system can Connector is faulty
operated even if the operator is not seated Connector cable is damaged
in operator seat Unload solenoid is broken
Controller is broken
F1-1 Combination meter abnormal Problem on the display Connector is damaged
F1-2 Hour meter cable is damaged
Hour meter is broken
Controller is broken
F4-1~8 CPU error CPU abnormal Multi-function board
broken display
H1-1 Lift lever potentiometer abnormal Lift cannot operate Connectro is faulty
H1-2 The potentiometer wire is damaged
H1-3 Potentiometer is broken
H1-4 Controller is broken
H1-5 Fuse blown
H2-1 Tilt lever potentiometer abnormal Tilt does not operate Connectro is faulty
H2-2 The potentiometer wire is damaged
H2-3 Potentiometer is broken
H2-4 Controller is broken
H2-5 Fuse blown
H3-1 Attachment 1 lever potentiometer Attachment 1 does not operate Connectro is faulty
H3-2 abnormal Potentiometer cable is damaged
H3-3 The potentiometer is faulty
H3-4 Controller is broken
H3-5 Fuse blown
H4-1 Attachment 2 lever potentiometer Attachment 2 does not operate Connectro is damaged
H4-2 abnormal Potentiometer cable is damaged
H4-3 The potentiometer is faulty
H4-4 Controller is broken
H4-5 Fuse blown
H5-1 Lift solenoid abnormal Elevator may not operate Faulty connector
H5-2 Elevator cable (PUSH) is damaged
Solenoid lift (PUSH) is broken
Elevator cable (PULL) is broken
Solenoid lift (PULL) is broken
Controller is broken
H6-1 Solenoid Tilt Abnormal Tilt may not operate Connector is faulty
H6-2 Faulty tilt (PUSH) cable
Solenoid tilt (PUSH) faulty
Broken tilt (PULL) cable
Solenoid tilt (PULL) faulty
Controller is broken
H7-1 Attachment 1 abnormal solenoid Attachment 1 may not work Connector is damaged
H7-2 operating Att 1 (PUSH) cable is faulty
Solenoid Att 1 (PUSH) is faulty
Att 1 (PULL) cable is damaged
Solenoid Att 1 (PULL) is faulty
Controller is broken
H8-1 Attachment 2 abnormal solenoid Attachment 2 may not work Connector is damaged
H8-2 operating Att 2 (PUSH) cable is faulty
Solenoid Att 2 (PUSH) is faulty
Att 2 (PULL) cable is damaged
Solenoid Att 2 (PULL) is faulty
Controller is broken
HA-1 3/4-way change relay abnormal Attachment transfer is not possible Connector is damaged
operating Relay cable 1 is damaged
Relay 1 is broken
Relay cable 2 is damaged
Relay 2 is broken
Controller is broken
Error mode Symptoms on forklift Possible causes
broken WARNING LIST
IF THE WRENCH LAMP IS ON AND WITH THESE SYMPTOMS BELOW ON
|
Indication |
Wrench lamp |
Spanner |
Detection ECU |
Error mode |
Phenomenon on vehicle |
|
01-01 |
01-01 |
Blinking |
4Y-ECS |
Fuel feedback control error (gasoline) rich |
The engine speed is unstable and it may stop. |
|
01-02 |
01-02 |
Blinking |
4Y-ECS |
Fuel feedback control error (gasoline) lean |
|
|
01-03 |
01-03 |
Blinking |
4Y-ECS |
Fuel feedback control error (LPG/CNG) rich |
|
|
01-04 |
01-04 |
Blinking |
4Y-ECS |
Fuel feedback control error (LPG/CNG) lean |
|
|
01-05 |
01-05 |
Blinking |
4Y-ECS |
02 sensor open abnormality |
The engine speed is unstable and it may stop. |
|
01-06 |
01-06 |
Blinking |
4Y-ECS |
02 sensor heater open abnormality |
Display only |
|
02-01 |
02-01 |
Blinking |
4Y-ECS |
Intake temperature sensor open abnormality |
The engine may have a problem at low temperatures. |
|
02-02 |
02-02 |
Blinking |
4Y-ECS |
Intake temperature sensor short abnormality |
|
|
03-01 |
03-01 |
Blinking |
4Y-ECS |
Intake pipe pressure sensor open abnormality |
The engine may have a problem |
|
03-02 |
03-02 |
Blinking |
4Y-ECS |
Intake pipe pressure sensor short abnormality |
|
|
04-01 |
04-01 |
Blinking |
4Y-ECS |
Coolant temperature sensor open abnormality |
The engine may have a problem at low temperatures. |
|
04-02 |
04-02 |
Blinking |
4Y-ECS |
Coolant temperature sensor short abnormality |
|
|
05-01 |
05-01 |
Blinking |
4Y-ECS |
Throttle position sensor 1 open abnormality |
Limting speed of traveling and materials handling due to limited engine power output |
|
05-02 |
05-02 |
Blinking |
4Y-ECS |
Throttle position sensor 1 short abnormality |
|
|
05-03 |
05-03 |
Blinking |
4Y-ECS |
Throttle position sensor 2 open abnormality |
|
|
05-04 |
05-04 |
Blinking |
4Y-ECS |
Throttle position sensor 2 short abnormality |
|
|
05-05 |
05-05 |
Blinking |
4Y-ECS |
Throttle position sensor offset abnormality |
|
|
05-06 |
05-06 |
Blinking |
4Y-ECS |
Throttle position sensor out of range error |
|
|
06-01 |
06-01 |
Blinking |
4Y-ECS |
Throttle motor drive circuit open abnormality |
Limting speed of traveling and materials handling due to limited engine power output |
|
06-02 |
06-02 |
Blinking |
4Y-ECS |
Throttle motor drive circuit short abnormality |
|
|
06-03 |
06-03 |
Blinking |
4Y-ECS |
Throttle motor power supply circuit open abnormality |
|
|
06-04 |
06-04 |
Blinking |
4Y-ECS |
Throttle motor power supply circuit short abnormality |
|
|
06-05 |
06-05 |
Blinking |
4Y-ECS |
Throttle motor seizing abnormality |
|
|
06-06 |
06-06 |
Blinking |
4Y-ECS |
Electronic throttle system error |
|
|
07-01 |
07-01 |
Blinking |
4Y-ECS |
Air-fuel ratio motor open abnormality |
The engine speed is unstable and it may stop. |
|
08-01 |
08-01 |
Blinking |
4Y-ECS |
Low voltage (battery line open) error |
Display only |
|
09-01 |
09-01 |
Blinking |
4Y-ECS |
Ignition signal error |
The engine speed is unstable and it may stop. |
|
OA-1 |
OA-1 |
Blinking |
4Y-ECS |
Fuel specification determination signal error |
Display only |
|
OA-2 |
OA-2 |
Blinking |
4Y-ECS |
Fuel specification changeover switch error |
Display only |
|
OA-3 |
OA-3 |
Blinking |
4Y-ECS |
Fuel specification type unmatch |
Engine may stop |
|
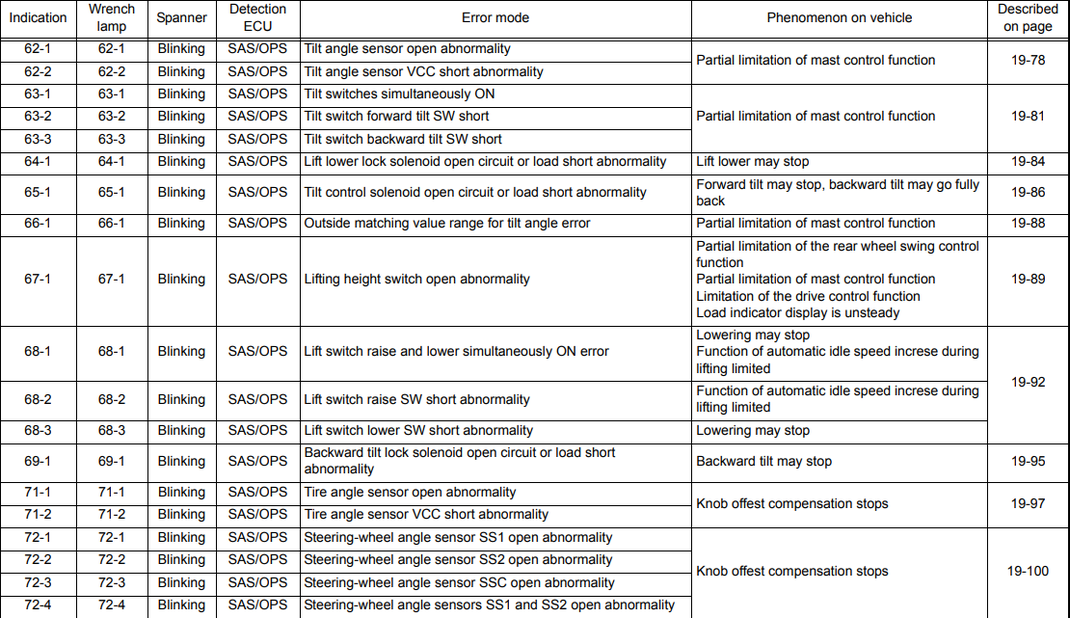
62-1 |
62-1 |
Blinking |
SAS/OPS |
Tilt angle sensor open abnormality |
Partial limitation of mast control function |
|
62-2 |
62-2 |
Blinking |
SAS/OPS |
Tilt angle sensor VCC short abnormality |
|
|
63-1 |
63-1 |
Blinking |
SAS/OPS |
Tilt switches simultaneously ON |
Partial limitation of mast control function |
|
63-2 |
63-2 |
Blinking |
SAS/OPS |
Tilt switch forward tilt SW short |
|
|
63-3 |
63-3 |
Blinking |
SAS/OPS |
Tilt switch backward tilt SW short |
|
|
64-1 |
64-1 |
Blinking |
SAS/OPS |
Lift lower lock solenoid open circuit or load short abnormality |
Lift lower may stop |
|
65-1 |
65-1 |
Blinking |
SAS/OPS |
Tilt control solenoid open circuit or load short abnormality |
Forward tilt may stop, backward tilt may go fully back |
|
66-1 |
66-1 |
Blinking |
SAS/OPS |
Outside matching value range for tilt angle error |
Partial limitation of mast control function |
|
67-1 |
67-1 |
Blinking |
SAS/OPS |
Lifting height switch open abnormality |
Partial limitation of the rear wheel swing control function |
|
68-1 |
68-1 |
Blinking |
SAS/OPS |
Lift switch raise and lower simultaneously ON error |
Lowering may stop |
|
68-2 |
68-2 |
Blinking |
SAS/OPS |
Lift switch raise SW short abnormality |
Function of automatic idle speed increse during lifting limited |
|
68-3 |
68-3 |
Blinking |
SAS/OPS |
Lift switch lower SW short abnormality |
Lowering may stop |
|
69-1 |
69-1 |
Blinking |
SAS/OPS |
Backward tilt lock solenoid open circuit or load short abnormality |
Backward tilt may stop |
|
71-1 |
71-1 |
Blinking |
SAS/OPS |
Tire angle sensor open abnormality |
Knob offest compensation stops |
|
71-2 |
71-2 |
Blinking |
SAS/OPS |
Tire angle sensor VCC short abnormality |
|
|
72-1 |
72-1 |
Blinking |
SAS/OPS |
Steering-wheel angle sensor SS1 open abnormality |
Knob offest compensation stops |
|
72-2 |
72-2 |
Blinking |
SAS/OPS |
Steering-wheel angle sensor SS2 open abnormality |
|
|
72-3 |
72-3 |
Blinking |
SAS/OPS |
Steering-wheel angle sensor SSC open abnormality |
|
|
72-4 |
72-4 |
Blinking |
SAS/OPS |
Steering-wheel angle sensors S51 and SS2 open abnormality |
|
Indication |
Wrench lamp |
Spanner |
Detection ECU |
Error mode |
Phenomenon on vehicle |
|
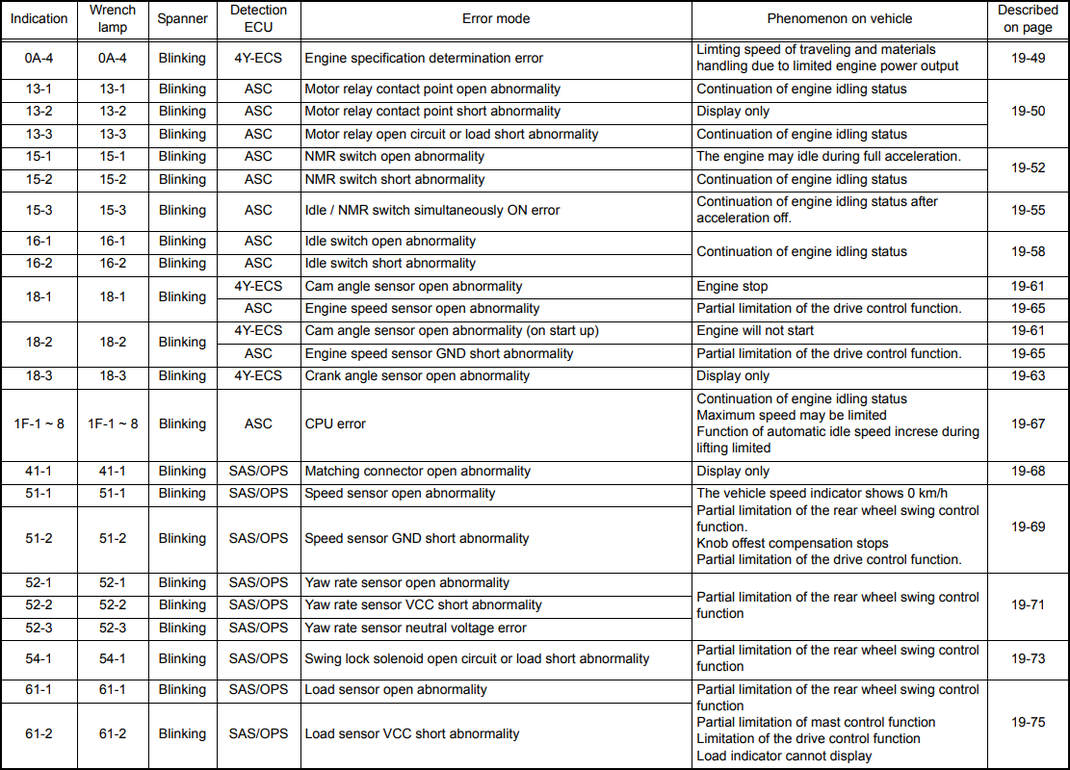
OA-4 |
OA-4 |
Blinking |
4Y-ECS |
Engine specification determination error |
Limting speed of traveling and materials handling due to limited engine power output |
|
13-1 |
13-1 |
Blinking |
ASC |
Motor relay contact point open abnormality |
Continuation of engine idling status |
|
13-2 |
13-2 |
Blinking |
ASC |
Motor relay contact point short abnormality |
Display only |
|
13-3 |
13-3 |
Blinking |
ASC |
Motor relay open circuit or load short abnormality |
Continuation of engine idling status |
|
15-1 |
15-1 |
Blinking |
ASC |
NMR switch open abnormality |
The engine may idle during full acceleration. |
|
15-2 |
15-2 |
Blinking |
ASC |
NMR switch short abnormality |
Continuation of engine idling status |
|
15-3 |
15-3 |
Blinking |
ASC |
Idle / NMR switch simultaneously ON error |
Continuation of engine idling status after acceleration off. |
|
16-1 |
16-1 |
Blinking |
ASC |
Idle switch open abnormality |
Continuation of engine idling status |
|
16-2 |
16-2 |
Blinking |
ASC |
Idle switch short abnormality |
|
|
18-1 |
18-1 |
Blinking |
4Y-ECS |
Cam angle sensor open abnormality |
Engine stop |
|
ASC |
Engine speed sensor open abnormality |
Partial limitation of the drive control function. |
|||
|
18-2 |
18-2 |
Blinking |
4Y-ECS |
Cam angle sensor open abnormality (on start up) |
Engine will not start |
|
ASC |
Engine speed sensor GND short abnormality |
Partial limitation of the drive control function. |
|||
|
18-3 |
18-3 |
Blinking |
4Y-ECS |
Crank angle sensor open abnormality |
Display only |
|
1 F-1 — 8 |
1 F-1 — 8 |
Blinking |
ASC |
CPU error |
Continuation of engine idling status |
|
41-1 |
41-1 |
Blinking |
SAS/OPS |
Matching connector open abnormality |
Display only |
|
51-1 |
51-1 |
Blinking |
SAS/OPS |
Speed sensor open abnormality |
The vehicle speed indicator shows 0 km/h Partial limitation of the rear wheel swing control function. |
|
51-2 |
51-2 |
Blinking |
SAS/OPS |
Speed sensor GND short abnormality |
|
|
52-1 |
52-1 |
Blinking |
SAS/OPS |
Yaw rate sensor open abnormality |
Partial limitation of the rear wheel swing control function |
|
52-2 |
52-2 |
Blinking |
SAS/OPS |
Yaw rate sensor VCC short abnormality |
|
|
52-3 |
52-3 |
Blinking |
SAS/OPS |
Yaw rate sensor neutral voltage error |
|
|
54-1 |
54-1 |
Blinking |
SAS/OPS |
Swing lock solenoid open circuit or load short abnormality |
Partial limitation of the rear wheel swing control function |
|
61-1 |
61-1 |
Blinking |
SAS/OPS |
Load sensor open abnormality |
Partial limitation of the rear wheel swing control function |
|
61-2 |
61-2 |
Blinking |
SAS/OPS |
Load sensor VCC short abnormality |
|
Indication |
lamp lamp |
Spanner |
Detection ECU |
Error mode |
Phenomenon on vehicle |
|
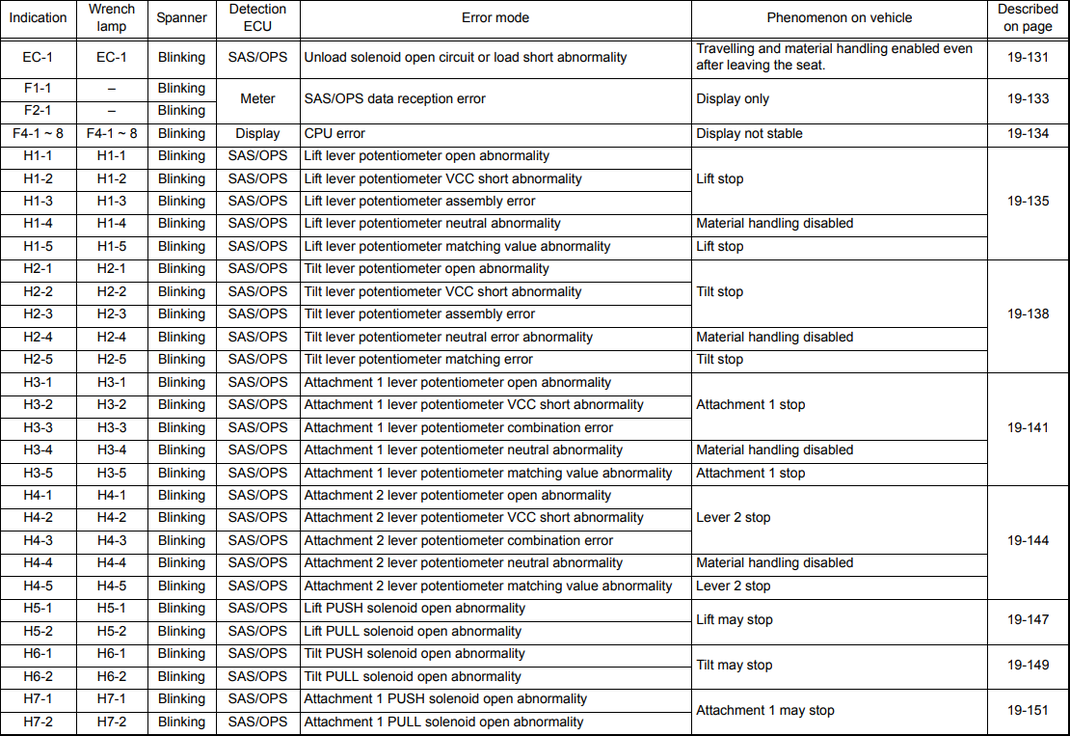
EC-1 |
EC-1 |
Blinking |
SAS/OPS |
Unload solenoid open circuit or load short abnormality |
Travelling and material handling enabled even after leaving the seat. |
|
F1-1 |
— |
Blinking |
Meter |
SAS/OPS data reception error |
Display only |
|
F2-1 |
— |
Blinking |
|||
|
F4-1 — 8 |
F4-1 — 8 |
Blinking |
Display |
CPU error |
Display not stable |
|
H1-1 |
H1-1 |
Blinking |
SAS/OPS |
Lift lever potentiometer open abnormality |
Lift stop |
|
H1-2 |
H1-2 |
Blinking |
SAS/OPS |
Lift lever potentiometer VCC short abnormality |
|
|
H1-3 |
H1-3 |
Blinking |
SAS/OPS |
Lift lever potentiometer assembly error |
|
|
H1-4 |
H1-4 |
Blinking |
SAS/OPS |
Lift lever potentiometer neutral abnormality |
Material handling disabled |
|
H1-5 |
H1-5 |
Blinking |
SAS/OPS |
Lift lever potentiometer matching value abnormality |
Lift stop |
|
H2-1 |
H2-1 |
Blinking |
SAS/OPS |
Tilt lever potentiometer open abnormality |
Tilt stop |
|
H2-2 |
H2-2 |
Blinking |
SAS/OPS |
Tilt lever potentiometer VCC short abnormality |
|
|
H2-3 |
H2-3 |
Blinking |
SAS/OPS |
Tilt lever potentiometer assembly error |
|
|
H2-4 |
H2-4 |
Blinking |
SAS/OPS |
Tilt lever potentiometer neutral error abnormality |
Material handling disabled |
|
H2-5 |
H2-5 |
Blinking |
SAS/OPS |
Tilt lever potentiometer matching error |
Tilt stop |
|
H3-1 |
H3-1 |
Blinking |
SAS/OPS |
Attachment 1 lever potentiometer open abnormality |
Attachment 1 stop |
|
H3-2 |
I-13-2 |
Blinking |
SAS/OPS |
Attachment 1 lever potentiometer VCC short abnormality |
|
|
H3-3 |
H3-3 |
Blinking |
SAS/OPS |
Attachment 1 lever potentiometer combination error |
|
|
H3-4 |
H3-4 |
Blinking |
SAS/OPS |
Attachment 1 lever potentiometer neutral abnormality |
Material handling disabled |
|
H3-5 |
H3-5 |
Blinking |
SAS/OPS |
Attachment 1 lever potentiometer matching value abnormality |
Attachment 1 stop |
|
H4-1 |
H4-1 |
Blinking |
SAS/OPS |
Attachment 2 lever potentiometer open abnormality |
Lever 2 stop |
|
H4-2 |
H4-2 |
Blinking |
SAS/OPS |
Attachment 2 lever potentiometer VCC short abnormality |
|
|
H4-3 |
H4-3 |
Blinking |
SAS/OPS |
Attachment 2 lever potentiometer combination error |
|
|
H4-4 |
H4-4 |
Blinking |
SAS/OPS |
Attachment 2 lever potentiometer neutral abnormality |
Material handling disabled |
|
H4-5 |
H4-5 |
Blinking |
SAS/OPS |
Attachment 2 lever potentiometer matching value abnormality |
Lever 2 stop |
|
H5-1 |
H5-1 |
Blinking |
SAS/OPS |
Lift PUSH solenoid open abnormality |
Lift may stop |
|
H5-2 |
H5-2 |
Blinking |
SAS/OPS |
Lift PULL solenoid open abnormality |
|
|
H6-1 |
H6-1 |
Blinking |
SAS/OPS |
Tilt PUSH solenoid open abnormality |
Tilt may stop |
|
H6-2 |
H6-2 |
Blinking |
SAS/OPS |
Tilt PULL solenoid open abnormality |
|
|
H7-1 |
H7-1 |
Blinking |
SAS/OPS |
Attachment 1 PUSH solenoid open abnormality |
Attachment 1 may stop |
|
H7-2 |
H7-2 |
Blinking |
SAS/OPS |
Attachment 1 PULL solenoid open abnormality |
|
Indication |
Wrench lamp |
Spanner |
Detection ECU |
Error mode |
Phenomenon on vehicle |
|
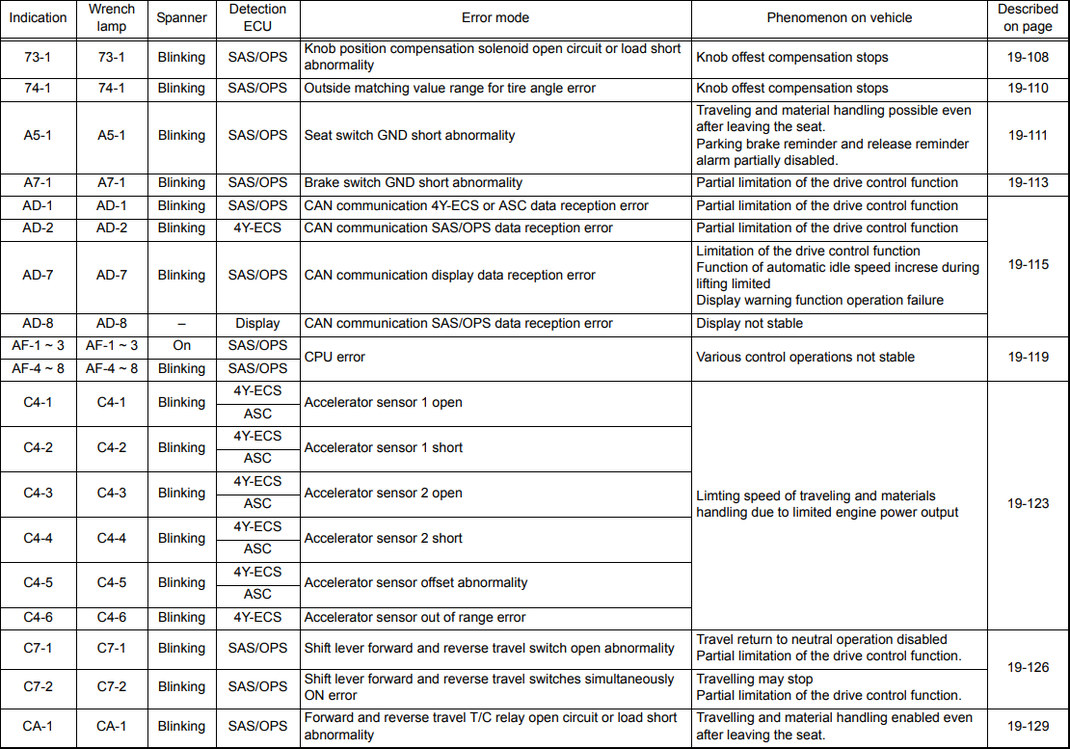
73-1 |
73-1 |
Blinking |
SAS/OPS |
Knob position compensation solenoid open circuit or load short abnormality |
Knob offest compensation stops |
|
74-1 |
74-1 |
Blinking |
SAS/OPS |
Outside matching value range for tire angle error |
Knob offest compensation stops |
|
A5-1 |
A5-1 |
Blinking |
SAS/OPS |
Seat switch GND short abnormality |
Traveling and material handling possible even after leaving the seat. |
|
A7-1 |
A7-1 |
Blinking |
SAS/OPS |
Brake switch GND short abnormality |
Partial limitation of the drive control function |
|
AD-1 |
AD-1 |
Blinking |
SAS/OPS |
CAN communication 4Y-ECS or ASC data reception error |
Partial limitation of the drive control function |
|
AD-2 |
AD-2 |
Blinking |
4Y-ECS |
CAN communication SAS/OPS data reception error |
Partial limitation of the drive control function |
|
AD-7 |
AD-7 |
Blinking |
SAS/OPS |
CAN communication display data reception error |
Limitation of the drive control function |
|
AD-8 |
AD-8 |
Display |
CAN communication SAS/OPS data reception error |
Display not stable |
|
|
AF-1 — 3 |
AF-1 — 3 |
On |
SAS/OPS |
CPU error |
Various control operations not stable |
|
AF-4 — 8 |
AF-4 — 8 |
Blinking |
SAS/OPS |
||
|
C4-1 |
C4-1 |
Blinking |
4Y-ECS |
Accelerator sensor 1 open |
Limting speed of traveling and materials handling due to limited engine power output |
|
ASC |
|||||
|
C4-2 |
C4-2 |
Blinking |
4Y-ECS |
Accelerator sensor 1 short |
|
|
ASC |
|||||
|
C4-3 |
C4-3 |
Blinking |
4Y-ECS |
Accelerator sensor 2 open |
|
|
ASC |
|||||
|
C4-4 |
C4-4 |
Blinking |
4Y-ECS |
Accelerator sensor 2 short |
|
|
ASC |
|||||
|
C4-5 |
C4-5 |
Blinking |
4Y-ECS |
Accelerator sensor offset abnormality |
|
|
ASC |
|||||
|
C4-6 |
C4-6 |
Blinking |
4Y-ECS |
Accelerator sensor out of range error |
|
|
C7-1 |
C7-1 |
Blinking |
SAS/OPS |
Shift lever forward and reverse travel switch open abnormality |
Travel return to neutral operation disabled Partial limitation of the drive control function. |
|
C7-2 |
C7-2 |
Blinking |
SAS/OPS |
Shift lever forward and reverse travel switches simultaneously ON error |
Travelling may stop |
|
CA-1 |
CA-1 |
Blinking |
SAS/OPS |
Forward and reverse travel T/C relay open circuit or load short abnormality |
Travelling and material handling enabled even after leaving the seat. |
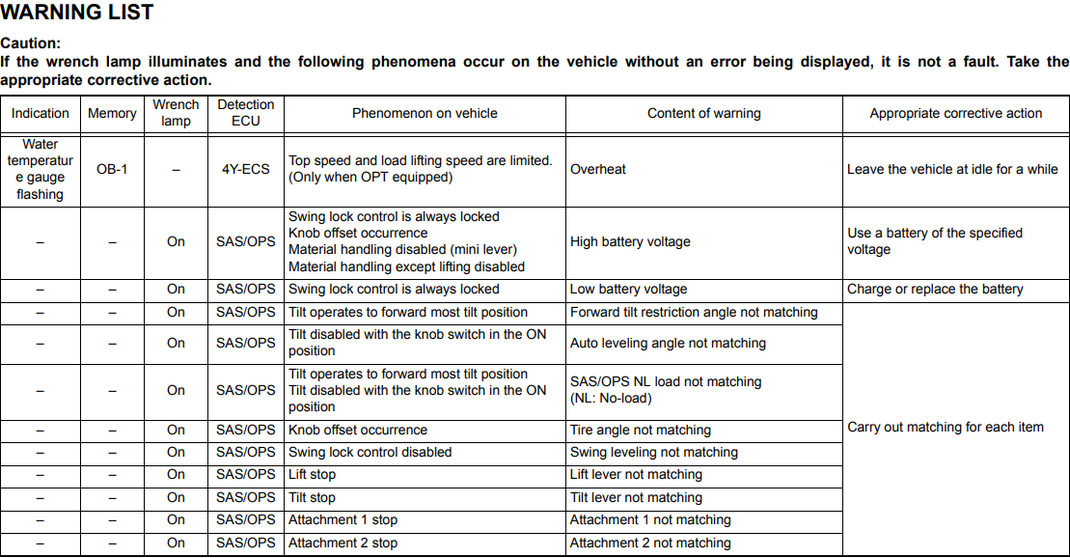
Caution:
If the wrench lamp illuminates and the following phenomena occur on the vehicle without an error being displayed, it is not a fault. Take the appropriate corrective action.
|
Indication |
Memory |
Wrench lamp |
Detection ECU |
Phenomenon on vehicle |
Content of warning |
Appropriate corrective action |
|
Water temperatur e gauge flashing |
OB-1 |
— |
4Y-ECS |
Top speed and load lifting speed are limited. (Only when OPT equipped) |
Overheat |
Leave the vehicle at idle for a while |
|
— |
— |
On |
SAS/OPS |
Swing lock control is always locked Knob offset occurrence |
High battery voltage |
Use a battery of the specified voltage |
|
— |
— |
On |
SAS/OPS |
Swing lock control is always locked |
Low battery voltage |
Charge or replace the battery |
|
— |
— |
On |
SAS/OPS |
Tilt operates to forward most tilt position |
Forward tilt restriction angle not matching |
Carry out matching for each item |
|
— |
— |
On |
SAS/OPS |
Tilt disabled with the knob switch in the ON position |
Auto leveling angle not matching |
|
|
— |
— |
On |
SAS/OPS |
Tilt operates to forward most tilt position Tilt disabled with the knob switch in the ON position |
SAS/OPS NIL load not matching (NL: No-load) |
|
|
— |
— |
On |
SAS/OPS |
Knob offset occurrence |
Tire angle not matching |
|
|
— |
— |
On |
SAS/OPS |
Swing lock control disabled |
Swing leveling not matching |
|
|
— |
— |
On |
SAS/OPS |
Lift stop |
Lift lever not matching |
|
|
— |
— |
On |
SAS/OPS |
Tilt stop |
Tilt lever not matching |
|
|
— |
— |
On |
SAS/OPS |
Attachment 1 stop |
Attachment 1 not matching |
|
|
— |
— |
On |
SAS/OPS |
Attachment 2 stop |
Attachment 2 not matching |

- Manuals
- Brands
- Toyota Manuals
- Forklifts
- BT Levio W Series
- Product manual
-
Contents
-
Table of Contents
-
Bookmarks
Quick Links
Product guide
W-series
LWE140
LWE160
LWE180
LWE200
LWE250
www.toyota-forklifts.eu
Related Manuals for Toyota BT Levio W Series
Summary of Contents for Toyota BT Levio W Series
-
Page 1
Product guide W-series LWE140 LWE160 LWE180 LWE200 LWE250 www.toyota-forklifts.eu… -
Page 2
This product guide applies to: Model F code TD code LWE140 838aa LWE160 838ab LWE180 838ac LWE200 839aa LWE250 840aa Document revision history: Edition date Changes April 2008 Next generation Low-lifters February 2011 Technical updates August, 2011 New family and series name Januare, 2012 Technical updates Part number: 749851-040… -
Page 3: Table Of Contents
Contents Reading instructions Product range information BT Levio W-series (Low-lifter Walkie Electric) … … …… …… … …… … …… 9 LWE140 … ………… …… … …… … …… … …… …… … …… … …… 11 LWE160 … ………… … …… …… … …… … …… … …… …… … …… 11 LWE180 ……
-
Page 4
Product details Operator environment … ……… …… … …… … …… … …… …… … …… 25 Battery covers and storage compartments …… … …… …… … …… … …… 30 Driving features/programming the truck … …… … …… …… … …… … …… 31 Motor and power pack ………… -
Page 5
Options Battery change from the side … …… … …… … …… … …… …… … …… 65 Battery change table … … …… …… … …… … …… … …… …… … …… 66 Extra battery cables … … …… …… … …… … …… … …… …… … …… 66 Battery change cable …… -
Page 6
Product guide – BT Levio W-series… -
Page 7
Reading instructions This product guide is designed as a point of reference. To facilitate searching for specific features, it has an index at the back. In some cases, information is avail- able in two different chapters. This applies especially to the Sales arguments and Product details chapters describing the various features and benefits of the truck. -
Page 8
Product guide – BT Levio W-series… -
Page 9: Product Range Information
Product range information Product range information BT Levio W-series (Low-lifter Walkie Electric) BT Levio W-series without platform is a complete low-lifter series for walkie applications. These machines are mainly used where space is limited and travel distances are relatively short. All models have a maximum speed of 6 km/h. LWE200 can, as an option, be equipped with operator platform.
-
Page 10
Product range information intended application: Type of truck Capacity Feature LWE = Low-lifter Walkie Electrical 140 = 1400 kg L = Low-lifter W = Walkie 160 = 1600 kg E = Electrical 180 = 1800 kg 200 = 2000 kg 250 = 2500 kg The model code indicates rated truck capacity. -
Page 11: Lwe140
Product range information LWE140 ● BT Castor link. ● 156 mm narrow fork carriage. ● Chassis width 726 mm. ● Small standard battery compartment only, 150 Ah battery. ● l measurement 481 mm. ● Ideal for applications in smaller shops and warehouses.
-
Page 12: Lwe180
Product range information LWE180 ● BT Castor link. ● 180 mm standard fork carriage. ● Chassis width 726 mm. ● Medium or large standard battery com- partment, 225/300 Ah battery. ● l measurement 538/588 mm. ● Ideal for applications in warehouses and distribution centres.
-
Page 13: Lwe250
Product range information LWE250 ● BT Castor link. ● 180 mm standard fork carriage. ● Reinforced fork carriage. ● Chassis width 726 mm. ● Medium or large standard battery com- partment, 225/300 Ah battery. ● Large battery with battery towards the side, 260 Ah battery.
-
Page 14
Product range information Product guide – BT Levio W-series… -
Page 15: Applications
Applications Applications Walking There is always an LWE truck version that is optimised for the application no matter whether this involves loading/unloading of lorries, horizontal transport and/ or order picking. These trucks are typically used in warehouses/distribution cen- tres, industrial applications and shops/supermarkets with short to medium transport distances (aprox.
-
Page 16: Industry
Applications Industry Industrial applications require trucks with a high level of reliability. Goods must always be in the right place when needed. An increasing trend at many manufacturing companies is to reduce ware- house surfaces and intensify incoming deliveries. Although incoming deliveries may be frequent, usage intensity in these kinds of applications is lower compared to use in warehouses and distri- bution centres.
-
Page 17: Shops/Supermarkets
Applications Shops/supermarkets In shops and supermarkets, the trucks are often operated by inexperienced staff, and they may even be left unattended on shop floors among customers and children. This environment requires an easy-to-use truck designed to prevent unauthorised use. The LWE trucks feature simple operation, and they have a programmable switch-off timer.
-
Page 18: Which Truck For Which Application
Applications Which truck for which application? The following factors determine which model is suited for a given application: — Load carrier and load centre distance — Capacity — Usage intensity — Travel distances — Aisle widths — Ramps/slopes — Floor conditions It is also recommended to explore environmental requirements and future plans, for example to choose a truck that will not become obsolete when the company expands.
-
Page 19: Sales Arguments
Sales arguments Sales arguments In fall 2007, BT carried out market research with participation from 300 respond- ents across Europe, all of them potential customers. The results from this survey points to three important criteria for this kind of truck: ●…
-
Page 20: Simplicity
Sales arguments Simplicity These trucks are regarded as a tool. The intention is that both experienced and in- experienced operators should be able to use them. The following features make the LWE series trucks easy to operate: Manoeuvrability Feature ● The LWE trucks has a 5-point wheel configura- tion, i.e.
-
Page 21
Sales arguments View Feature The LWE trucks have a well-arranged ex- ternal design with superior operator view thanks to: ● A compact truck body that is lower on the fork side. ● Optimum distance to the truck with the operator sufficiently close to the truck for an unobstructed view. -
Page 22: Safety
Sales arguments Safety A safe truck prevents injuries and reduces costly damage to goods and the truck. The LWE series trucks come with a number of features that makes them safe in use. Operator safety Feature ● The distance to the operator’s feet is consider- able and floor clearance is 35 mm.
-
Page 23: Durability
Sales arguments Durability A truck that cannot be used costs money. On one hand the truck must always be available when needed in order for business to continue as usual and remain ef- ficient, while on the other hand service costs often represent a significant share of total truck costs during the truck’s life cycle.
-
Page 24
Sales arguments Benefit By designing for durability to eliminate causes of trouble, the following has been achieved: ● Unscheduled downtime that causes business interruptions has been reduced. ● Unnecessary repair costs have been reduced. ● Truck service life has been extended. Quick and easy service Feature In the design of the LWE trucks, a high level of serviceability was a key focus:… -
Page 25: Product Details
Product details Product details Operator environment The LWE trucks are primarily designed for operators walking alongside the truck and not standing on a platform, however, the LWE200 can be ordered with optional platform. Tiller arm and controls There are two versions of the tiller arm for the LWE series. One is designed for the walkie versions while the other is designed for the platform versions with the op- erator riding onboard.
-
Page 26
Product details Feature All controls are within easy reach and not placed too close together. The truck and all truck opera- tions can be operated with a single hand, left or right, as preferred. Benefit All controls are within immediate reach to reduce the risk of repetitive strain injury while opening up the possibility of productivity gains thanks to improved efficiency. -
Page 27
Product details Benefit No matter whether the truck is protected by a PIN code or ID unit: ● The truck can always be guarded against unauthorised use. ● Up to ten different operator settings can be stored in truck memory. Some companies prefer a physical key, in case an ID key, for truck access in order to keep track of who is using the trucks, especially in cases where external opera- tors need to temporarily use the truck, while others prefer access via PIN codes that… -
Page 28
Product details Feature When upright, the arm remains within the truck profile. Benefit The tiller arm does not require any space when left in the upright position, a clear advantage in very tight spaces. Feature The tiller arm features safety reversing. When the safety reversing switch is pushed, the trucks stops and immediately reverses in the other direction. -
Page 29
Product details Display The display shows battery status, total travel time and error messages. The display is also used to program operator parameters. Normal- ly, battery capacity is displayed as a percentage (%), but can when needed be replaced by error codes or operator parameters. -
Page 30: Battery Covers And Storage Compartments
Product details Benefit ● The operator can quickly confirm whether something is wrong with the truck, and he can in some cases correct it by restarting the truck. ● If intervention by a service technician is required, he can be informed about what’s wrong with the truck before arriving on site.
-
Page 31: Driving Features/Programming The Truck
Product details Driving features/programming the truck The LWE trucks are highly manoeuvrable and offer indi- vidual setting options for the operators. Settings that the operator can change himself are called operator parame- ters. The trucks also have a machine register in which set- tings only can be changed by a service technician.
-
Page 32
Product details Operator parameters To reprogram operator-specific parameters (if the change is permitted), proceed as follows: ● Press the horn button and keep it pressed while starting the truck using either PIN code entry or the ID unit. ● Release the horn button when the display shows “P”. The parameter symbol on the display lights. -
Page 33
Product details Feature It is possible to adapt the settings for speed, acceleration and braking characteris- tics to the operator’s level of experience and/or preferences. The truck can store up to ten different settings. Benefit By adapting the truck to the operator and/or the application, damage caused by in- experienced operators can be reduced while maximum productivity can be achieved with experienced operators. -
Page 34
Product details Automatic switch-off For more information regarding automatic switch-off, see the Service manual. Feature A service technician can set the desired time in- terval for truck switch-off in case the truck is left unattended. This time can be set to either 4 h or in the range of 1-20 minutes in increments of one minute. -
Page 35
Product details Brakes During normal travel, the motor is used to brake the truck, however, it also has an electromechanical parking brake which is applied whenever the truck is not in use. The parking brake can be released by to screws. See service manual for more information. -
Page 36: Motor And Power Pack
Product details Feature When the speed control is released to the neutral position or when the travel direc- tion changes, the motor brake is automatically applied. Benefit This makes truck travel more gentle and reduces brake plate wear. Feature During normal truck travel when the motor is used to brake the truck, energy is regenerated and returned to the battery every time the truck brakes.
-
Page 37
Product details AC drive motor The size of the motor depends on the truck: ● The LWE140, LWE160 and LWE180 use 1.0 kW drive motors. ● The LWE200 and LWE250 use 1.5 kW drive motors. Feature The drive motor is permanentnly mounted, and the motor does not move when the drive wheel turns. -
Page 38
Product details BT Powerdrive system The BT Powerdrive system on the LWE series is a unique combination of contact- less controls, CAN bus communication (CAN = Controller Area Network) and AC drive motor. Feature Contactless controls Benefit High reliability and reduced downtime thanks to the reduced number of moving parts and wear points. -
Page 39: Drive Wheel
Product details Drive wheel The drive wheel diameter is 230 mm. The LWE models offer four different mate- rial types. Drive wheel material The choice of drive wheel is a matter of balancing price, road holding characteris- tics and load handling performance. Four different types of materials are available: Topthane, Vulkollan, Powerfriction and Vulkollan mixed with sand.
-
Page 40
Product details 3. Powerfriction Feature All models can be ordered with Powerfriction drive wheels. This is a non-marking material with high friction coefficient. Benefit Powerfriction provides excellent grip, even on moist surfaces, and has superior wear characteristics. It does not leave marks on floors. 4. -
Page 41
Product details Drive wheel bracket All models feature fixed mounting of the drive wheel with suspended castor wheels. For details, please refer to Castor wheels and BT Castor link. Feature The LWE trucks have a 5-point wheel con- figuration with the drive wheel in the cen- tre. -
Page 42: Electronic Components
Product details Electronic components A general design objective of the LWE series, was to use as few electric compo- nents and cables as possible, while remaining parts are optimally protected against dirt, humidity, impacts, etc. Feature MQS (Micro Quadlok System) terminals are used throughout.
-
Page 43: Cover
Product details Cover Feature The cover is made of a highly resistant ABS material and is secured with only two screws. Two different covers exist, one for the walkie models and one for trucks with the platform op- tion. Benefit The cover is easy to remove and provides easy access to truck components.
-
Page 44
Product details Feature The lower part of the frame is compression- moulded. Benefit The moulding makes the truck more rigid while it absorbs impacts in an area where it is most needed, thus protecting the various truck func- tions. Feature Floor clearance, i.e. -
Page 45: Castor Wheels
Product details Castor wheels The castor wheels have a width of 50 mm. It is possible to select between Vulkollan and Polyurethane as castor wheel material. Depending on the application, the load on the wheel suspension is handled differently. 3 different types of BT Castor Link are available, but they all rely on the same basic principle.
-
Page 46
Product details Feature When the truck turns or passes a bump, pressure increases on one castor wheel as a result of compression of the spring. Thanks to the torsion tube, the other spring will compress by an identical amount. Benefit The truck remains stable and will never start to rock and travel like a ‘walking duck’, a classic phenomenon when spring forces do not interact. -
Page 47: Fork Carriage
Product details Fork carriage As far as the fork carriage is concerned, all bushings and axles, both classic prob- lem sources, have been improved. This chapter describes these parts together with the forks and fork wheels. Two fork carriages are used, narrow and standard. Feature Narrow fork carriage with 156 mm wide forks.
-
Page 48
Product details Axles and bushings Because bushings and axles are highly vulnerable parts, new high-quality materials have been developed for the LWE and SWE truck series. The results from truck life cycle tests have been very positive. Feature The bushings are made from Teflon-coated composite material. Benefit Teflon-coated composite bushings offer extended length of service and do not re- quire lubrication. -
Page 49: Battery Compartments, Batteries And Chargers
Product details Battery compartments, batteries and chargers When selecting the battery, these aspects should be considered: ● Physical limitations of the battery compartment – information on battery com- partment sizes is available in the Technical information chapter. ● Minimum and maximum weight –- these weights are indicated in the Technical information chapter.
-
Page 50
Product details Feature It is possible to select a desired battery compartment size. On the larger models, battery replacement to the side is available as an option. Benefit The truck can be optimised for the intended application. For higher intensive ap- plications, lateral battery replacement is a recommended option. -
Page 51
Product details Battery connector and charging To charge the battery, disconnect the battery connector and connect it to the battery charger. The battery connector should also be disconnected in the following situa- tions to cut the power supply: ● In the event of an accident. ●… -
Page 52
Product details Feature Different types of chargers provide different characteristics: ● Conventional, unregulated chargers are sensitive to line voltage fluctuations. As a result, the charging duration can vary, however, these chargers are cost-effec- tive. ● HF chargers are not as sensitive to fluctuations in the line voltage, and they are able to carefully control the charging process and as a result the charging dura- tion. -
Page 53: Technical Information
Technical information Technical information Dimensions and performance figures x measurement The x measurement is the distance back●of●fork●to●the●fork●wheel●centre. For trucks with bogie wheels, it is measured from back●of●fork●to●fork●bogie-wheel● centre. Usually this measurement is available in the Product information. l measurement The l measurement is the Total●fork●length. measurement The l measurement is the Truck●length●including●back●of●fork.
-
Page 54
Technical information u measurement The u measurement is the distance between fork● tip● and● the● wheel-fork● pivot● point. T measurement The measurement from●back●of●forks●to●the●wheel●fork●pivot●point is called the T measurement. The T measurement can be calculated with the formula: T = l -u As an example the u and T measurements are important for long side handling of pallets. -
Page 55
Technical information Standard fork length tables LWE140/160 X down, Fl-u+119 X up, Fl-u+64 1000 1070 1120 1150 1200 1220 1019 1370 1085 1204 1149 1450 1165 1284 1229 1520 1235 1354 1299 LWE180/200/250 X down, Fl-u+116 X up, Fl-u+59 1000 1050 1070 1100… -
Page 56
Technical information e, b and b measurements LWE140 LWE160 LWE180 LWE200 LWE250 measurement, height of fork in lowered position measurement, height of fork in raised position. e measurement, fork width measurement, width over forks The b measurement is referred to as the width●over●forks. This measurement must suit the pallets to be handled by the truck. -
Page 57: Aisle Width Requirement
Technical information , turning radius The turning radius is the necessary Distance●to●turn●the●truck●around●a●virtual● point●referred●to●as●the●turning●centre with forks raised. The product informa- tion provides Wa measurements for all LWE truck versions. – Aisle width requirement The aisle width requirement can be described as the space required by the truck to pick a pallet from a pallet rack, reverse out in the aisle, turn and proceed down the aisle.
-
Page 58: Aisle Width Requirements
Technical information Aisle width requirements Truck Battery comp. Aisle width for pallets: LWE140 small 1420 1842 1000×1200 longside handling small 1420 1892 800×1200 shortside handling Truck Battery comp. Aisle width for pallets: LWE160 small 1420 1842 1000×1200 longside handling small 1420 1892 800×1200 shortside handling…
-
Page 59
Technical information Calculating A according to the standard, LWE range ● The values are from the Product information sheet for LWE200. Standard: A = 1447 + (1200 — 898) + 2×100 = 1949 Length of pallet must be substituted by total fork length Standard: A = 1447+ (1150 — 898) + 2×100 = 1899… -
Page 60: Pallets And Pallet Sizes
Technical information Pallets and pallet sizes 1200 Euro pallet 382,5 382,5 ● Outer dimensions: 800 × 1200 mm ● Pallet height: 144 mm 227,5 227,5 ● Height, fork entries: 100 all four sides ● Corners: 45° ● Pallet weight: approximately 27 kg ●…
-
Page 61: Choosing The Optimal Fork Specification
Technical information Choosing the optimal fork specification When forks suited for a pallet or a specific roll container, these items should be considered: ● The b measurement must suit the pallet /roll container to enable positioning of the forks between the pallet legs or between the wheels of the roll container. Example: With Width over Forks 450 mm and Fork Width 180 mm, only 90 mm remains between the forks and the truck will not be able to handle Euro pallets or Chep pallets.
-
Page 62: Battery Weights
Technical information Battery weights LWE140 Batt. compartment Min. batt. weight kg Max. batt. weight kg Capacity Ah Volt V Size L*W*H mm Small 651 x 150 x 570 LWE160 Batt. compartment Min. batt. weight kg Max. batt. weight kg Capacity Ah Volt V Size L*W*H mm Small 651 x 150 x 570 Medium…
-
Page 63: Battery And Charger
Technical information Battery and charger Information on Hawker Evolution GEL batteries Hawker Evolution GEL batteries is the only type of valve-regulated batteries of- fered for the trucks in the LWE series. Please note the following if selecting a bat- tery of this type for the truck: ●…
-
Page 64
Technical information Product guide – BT Levio W-series… -
Page 65: Options
Options Options To adapt the truck to customer preferences, a number of options are available. Battery change from the side Battery roller bed which enables lateral battery replacement (only for trucks with a large bat- tery compartment). Not available for LWE140, LWE160 and LWE180.
-
Page 66: Battery Change Table
Options Battery change table To facilitate battery change from the side, an exter- nal battery change table is also available. The height from the floor to the top of the rollers is adjustable. The battery change table measurments are 834 x 912 mm.
-
Page 67: Built-In Charger
Options Built-in charger When connected to 230 V, the charger has a capacity of 30 A.It is self-adjusting and can be used for voltages between 90 V and 255 V AC, 45 to 400 Hz. For voltages under 200 V, the output current will be reduced. Freely ventilated batteries up to 320 Ah and valve regulated batteries from 134 to 213 Ah can be charged.
-
Page 68: Spacer For Long Side Pallet Handling
Options Feature Any error codes generated by the battery charger are displayed on the display. Benefit This simplifies fault diagnosis if required. Feature When the built-in charger is used, it is not possible to charge the battery unless the battery cover is opened since the power cord needs to be pulled out from behind the cover.
-
Page 69: Truck Log Systems
Truck log systems Toyota I-site Toyota I-site is a truck log and fleet management system that provides possibili- ties to monitor truck usage and operator performance. Toyota I-site is offered a monthly fee basis where we provide a continual process of analysis and consul- tancy to customers and give them access to our knowledge and skills to help us build customer relations.
-
Page 70
Options If the shock sensor is included in the system, information about collisions and im- pacts can be viewed. By monitoring truck usage and operator performance, customers can improve op- erations and reduce cost. Access to different levels of information can be set for different users/functions in the company. -
Page 71: Integrated E-Bar With Optional Accessories
Options Integrated E-bar with optional accessories All trucks in the LWE series, except for those with small battery compartment, can be fitted with an optional E-bar. This is BT’s standard solution for mounting a writing holder, plastic film holder, computer terminal, PC, scanner or other electronic equipment required onboard the truck.
-
Page 72: Turtle Button
Options Turtle button The turtle button allows temporary reduction of speed. The default setting for speed reduction is – 50 %, i.e. the travel speed will be reduced to 3 km/h. If necessary, this can be reprogrammed by a service technician. Feature When the turtle button is pressed once, the truck enters the turtle mode and travels at reduced speed.
-
Page 73: Operator Platform
Options Operator platform An operator platform is a useful option if the travel distances are a bit longer and the operator wants to have the comfort of a stand-on platform. The LWE series offers two different platform types, one with a rubber mat and automatic fold-up and a cold-store version with a checkered plate and also automatic fold-up.
-
Page 74
Options Feature The cold-store version of the platform uses a checkered plate. Benefit The checkered plate assures good friction even in cold stores and also in foodstuff applications where operators often wear wet or slippery shoes. Feature The platform is secured to a frame with rounded corners. Benefit The frame offers numerous benefits: ●… -
Page 75: Load Support
Options Load support The optional load support is attached to the back of the forks and is available on all LWE trucks. Feature The load support has a height of 1500 mm (from the top of the forks). Benefit This added support protects the operator and goods.
-
Page 76: Rubber Border
Options Rubber border A rubber border is available for all BT Levio W-series models. The trucks can be ordered with a rubber border instead of the standard steel border to allow high gradient ramp handling ability. The rubber border is especially suited for applications with high thresholds, curbs and ramps with high gradients.
-
Page 77: Appendix
Appendix Appendix Environmental work within BT The BT trucks are produced at manufacturing sites where environmental issues are in focus. Waste management and reduction of hazardous chemicals used in production are natural parts of the everyday environmental work. We have been ISO 14001 certified since 1997, and in our continuous environmental work we put effort into reducing energy consumption on all levels, while we work with preven- tive actions to reduce pollution risks and the risk of biological danger.
-
Page 78: Focus On Quality Within Bt
Appendix Focus on quality within BT The Toyota Way is based on the Guiding Principles at Toyota. Its five core values express the beliefs and values used in the daily work: Challenge To maintain a long-term vision and meet all challenges with the courage and crea- tivity needed to realise that vision.
-
Page 79
Appendix Products and components are tested and evaluated throughout the development process, both in lab environments and field tests. As a complement to calculations, structural tests as well as life time tests are performed. Apart from the functional testing and control made on all products before delivery, product quality is continuously monitored during manufacturing through welding audits on components and product audits on completed trucks. -
Page 80: Certificates
Appendix Certificates Product guide – BT Levio W-series…
-
Page 81
Appendix Product guide – BT Levio W-series…

- Manuals
- Brands
- Toyota Manuals
- Forklifts
- BT Levio W Series
- Product manual
-
Contents
-
Table of Contents
-
Bookmarks
Quick Links
Product guide
W-series
LWE140
LWE160
LWE180
LWE200
LWE250
www.toyota-forklifts.eu
Related Manuals for Toyota BT Levio W Series
Summary of Contents for Toyota BT Levio W Series
-
Page 1
Product guide W-series LWE140 LWE160 LWE180 LWE200 LWE250 www.toyota-forklifts.eu… -
Page 2
This product guide applies to: Model F code TD code LWE140 838aa LWE160 838ab LWE180 838ac LWE200 839aa LWE250 840aa Document revision history: Edition date Changes April 2008 Next generation Low-lifters February 2011 Technical updates August, 2011 New family and series name Januare, 2012 Technical updates Part number: 749851-040… -
Page 3: Table Of Contents
Contents Reading instructions Product range information BT Levio W-series (Low-lifter Walkie Electric) … … …… …… … …… … …… 9 LWE140 … ………… …… … …… … …… … …… …… … …… … …… 11 LWE160 … ………… … …… …… … …… … …… … …… …… … …… 11 LWE180 ……
-
Page 4
Product details Operator environment … ……… …… … …… … …… … …… …… … …… 25 Battery covers and storage compartments …… … …… …… … …… … …… 30 Driving features/programming the truck … …… … …… …… … …… … …… 31 Motor and power pack ………… -
Page 5
Options Battery change from the side … …… … …… … …… … …… …… … …… 65 Battery change table … … …… …… … …… … …… … …… …… … …… 66 Extra battery cables … … …… …… … …… … …… … …… …… … …… 66 Battery change cable …… -
Page 6
Product guide – BT Levio W-series… -
Page 7
Reading instructions This product guide is designed as a point of reference. To facilitate searching for specific features, it has an index at the back. In some cases, information is avail- able in two different chapters. This applies especially to the Sales arguments and Product details chapters describing the various features and benefits of the truck. -
Page 8
Product guide – BT Levio W-series… -
Page 9: Product Range Information
Product range information Product range information BT Levio W-series (Low-lifter Walkie Electric) BT Levio W-series without platform is a complete low-lifter series for walkie applications. These machines are mainly used where space is limited and travel distances are relatively short. All models have a maximum speed of 6 km/h. LWE200 can, as an option, be equipped with operator platform.
-
Page 10
Product range information intended application: Type of truck Capacity Feature LWE = Low-lifter Walkie Electrical 140 = 1400 kg L = Low-lifter W = Walkie 160 = 1600 kg E = Electrical 180 = 1800 kg 200 = 2000 kg 250 = 2500 kg The model code indicates rated truck capacity. -
Page 11: Lwe140
Product range information LWE140 ● BT Castor link. ● 156 mm narrow fork carriage. ● Chassis width 726 mm. ● Small standard battery compartment only, 150 Ah battery. ● l measurement 481 mm. ● Ideal for applications in smaller shops and warehouses.
-
Page 12: Lwe180
Product range information LWE180 ● BT Castor link. ● 180 mm standard fork carriage. ● Chassis width 726 mm. ● Medium or large standard battery com- partment, 225/300 Ah battery. ● l measurement 538/588 mm. ● Ideal for applications in warehouses and distribution centres.
-
Page 13: Lwe250
Product range information LWE250 ● BT Castor link. ● 180 mm standard fork carriage. ● Reinforced fork carriage. ● Chassis width 726 mm. ● Medium or large standard battery com- partment, 225/300 Ah battery. ● Large battery with battery towards the side, 260 Ah battery.
-
Page 14
Product range information Product guide – BT Levio W-series… -
Page 15: Applications
Applications Applications Walking There is always an LWE truck version that is optimised for the application no matter whether this involves loading/unloading of lorries, horizontal transport and/ or order picking. These trucks are typically used in warehouses/distribution cen- tres, industrial applications and shops/supermarkets with short to medium transport distances (aprox.
-
Page 16: Industry
Applications Industry Industrial applications require trucks with a high level of reliability. Goods must always be in the right place when needed. An increasing trend at many manufacturing companies is to reduce ware- house surfaces and intensify incoming deliveries. Although incoming deliveries may be frequent, usage intensity in these kinds of applications is lower compared to use in warehouses and distri- bution centres.
-
Page 17: Shops/Supermarkets
Applications Shops/supermarkets In shops and supermarkets, the trucks are often operated by inexperienced staff, and they may even be left unattended on shop floors among customers and children. This environment requires an easy-to-use truck designed to prevent unauthorised use. The LWE trucks feature simple operation, and they have a programmable switch-off timer.
-
Page 18: Which Truck For Which Application
Applications Which truck for which application? The following factors determine which model is suited for a given application: — Load carrier and load centre distance — Capacity — Usage intensity — Travel distances — Aisle widths — Ramps/slopes — Floor conditions It is also recommended to explore environmental requirements and future plans, for example to choose a truck that will not become obsolete when the company expands.
-
Page 19: Sales Arguments
Sales arguments Sales arguments In fall 2007, BT carried out market research with participation from 300 respond- ents across Europe, all of them potential customers. The results from this survey points to three important criteria for this kind of truck: ●…
-
Page 20: Simplicity
Sales arguments Simplicity These trucks are regarded as a tool. The intention is that both experienced and in- experienced operators should be able to use them. The following features make the LWE series trucks easy to operate: Manoeuvrability Feature ● The LWE trucks has a 5-point wheel configura- tion, i.e.
-
Page 21
Sales arguments View Feature The LWE trucks have a well-arranged ex- ternal design with superior operator view thanks to: ● A compact truck body that is lower on the fork side. ● Optimum distance to the truck with the operator sufficiently close to the truck for an unobstructed view. -
Page 22: Safety
Sales arguments Safety A safe truck prevents injuries and reduces costly damage to goods and the truck. The LWE series trucks come with a number of features that makes them safe in use. Operator safety Feature ● The distance to the operator’s feet is consider- able and floor clearance is 35 mm.
-
Page 23: Durability
Sales arguments Durability A truck that cannot be used costs money. On one hand the truck must always be available when needed in order for business to continue as usual and remain ef- ficient, while on the other hand service costs often represent a significant share of total truck costs during the truck’s life cycle.
-
Page 24
Sales arguments Benefit By designing for durability to eliminate causes of trouble, the following has been achieved: ● Unscheduled downtime that causes business interruptions has been reduced. ● Unnecessary repair costs have been reduced. ● Truck service life has been extended. Quick and easy service Feature In the design of the LWE trucks, a high level of serviceability was a key focus:… -
Page 25: Product Details
Product details Product details Operator environment The LWE trucks are primarily designed for operators walking alongside the truck and not standing on a platform, however, the LWE200 can be ordered with optional platform. Tiller arm and controls There are two versions of the tiller arm for the LWE series. One is designed for the walkie versions while the other is designed for the platform versions with the op- erator riding onboard.
-
Page 26
Product details Feature All controls are within easy reach and not placed too close together. The truck and all truck opera- tions can be operated with a single hand, left or right, as preferred. Benefit All controls are within immediate reach to reduce the risk of repetitive strain injury while opening up the possibility of productivity gains thanks to improved efficiency. -
Page 27
Product details Benefit No matter whether the truck is protected by a PIN code or ID unit: ● The truck can always be guarded against unauthorised use. ● Up to ten different operator settings can be stored in truck memory. Some companies prefer a physical key, in case an ID key, for truck access in order to keep track of who is using the trucks, especially in cases where external opera- tors need to temporarily use the truck, while others prefer access via PIN codes that… -
Page 28
Product details Feature When upright, the arm remains within the truck profile. Benefit The tiller arm does not require any space when left in the upright position, a clear advantage in very tight spaces. Feature The tiller arm features safety reversing. When the safety reversing switch is pushed, the trucks stops and immediately reverses in the other direction. -
Page 29
Product details Display The display shows battery status, total travel time and error messages. The display is also used to program operator parameters. Normal- ly, battery capacity is displayed as a percentage (%), but can when needed be replaced by error codes or operator parameters. -
Page 30: Battery Covers And Storage Compartments
Product details Benefit ● The operator can quickly confirm whether something is wrong with the truck, and he can in some cases correct it by restarting the truck. ● If intervention by a service technician is required, he can be informed about what’s wrong with the truck before arriving on site.
-
Page 31: Driving Features/Programming The Truck
Product details Driving features/programming the truck The LWE trucks are highly manoeuvrable and offer indi- vidual setting options for the operators. Settings that the operator can change himself are called operator parame- ters. The trucks also have a machine register in which set- tings only can be changed by a service technician.
-
Page 32
Product details Operator parameters To reprogram operator-specific parameters (if the change is permitted), proceed as follows: ● Press the horn button and keep it pressed while starting the truck using either PIN code entry or the ID unit. ● Release the horn button when the display shows “P”. The parameter symbol on the display lights. -
Page 33
Product details Feature It is possible to adapt the settings for speed, acceleration and braking characteris- tics to the operator’s level of experience and/or preferences. The truck can store up to ten different settings. Benefit By adapting the truck to the operator and/or the application, damage caused by in- experienced operators can be reduced while maximum productivity can be achieved with experienced operators. -
Page 34
Product details Automatic switch-off For more information regarding automatic switch-off, see the Service manual. Feature A service technician can set the desired time in- terval for truck switch-off in case the truck is left unattended. This time can be set to either 4 h or in the range of 1-20 minutes in increments of one minute. -
Page 35
Product details Brakes During normal travel, the motor is used to brake the truck, however, it also has an electromechanical parking brake which is applied whenever the truck is not in use. The parking brake can be released by to screws. See service manual for more information. -
Page 36: Motor And Power Pack
Product details Feature When the speed control is released to the neutral position or when the travel direc- tion changes, the motor brake is automatically applied. Benefit This makes truck travel more gentle and reduces brake plate wear. Feature During normal truck travel when the motor is used to brake the truck, energy is regenerated and returned to the battery every time the truck brakes.
-
Page 37
Product details AC drive motor The size of the motor depends on the truck: ● The LWE140, LWE160 and LWE180 use 1.0 kW drive motors. ● The LWE200 and LWE250 use 1.5 kW drive motors. Feature The drive motor is permanentnly mounted, and the motor does not move when the drive wheel turns. -
Page 38
Product details BT Powerdrive system The BT Powerdrive system on the LWE series is a unique combination of contact- less controls, CAN bus communication (CAN = Controller Area Network) and AC drive motor. Feature Contactless controls Benefit High reliability and reduced downtime thanks to the reduced number of moving parts and wear points. -
Page 39: Drive Wheel
Product details Drive wheel The drive wheel diameter is 230 mm. The LWE models offer four different mate- rial types. Drive wheel material The choice of drive wheel is a matter of balancing price, road holding characteris- tics and load handling performance. Four different types of materials are available: Topthane, Vulkollan, Powerfriction and Vulkollan mixed with sand.
-
Page 40
Product details 3. Powerfriction Feature All models can be ordered with Powerfriction drive wheels. This is a non-marking material with high friction coefficient. Benefit Powerfriction provides excellent grip, even on moist surfaces, and has superior wear characteristics. It does not leave marks on floors. 4. -
Page 41
Product details Drive wheel bracket All models feature fixed mounting of the drive wheel with suspended castor wheels. For details, please refer to Castor wheels and BT Castor link. Feature The LWE trucks have a 5-point wheel con- figuration with the drive wheel in the cen- tre. -
Page 42: Electronic Components
Product details Electronic components A general design objective of the LWE series, was to use as few electric compo- nents and cables as possible, while remaining parts are optimally protected against dirt, humidity, impacts, etc. Feature MQS (Micro Quadlok System) terminals are used throughout.
-
Page 43: Cover
Product details Cover Feature The cover is made of a highly resistant ABS material and is secured with only two screws. Two different covers exist, one for the walkie models and one for trucks with the platform op- tion. Benefit The cover is easy to remove and provides easy access to truck components.
-
Page 44
Product details Feature The lower part of the frame is compression- moulded. Benefit The moulding makes the truck more rigid while it absorbs impacts in an area where it is most needed, thus protecting the various truck func- tions. Feature Floor clearance, i.e. -
Page 45: Castor Wheels
Product details Castor wheels The castor wheels have a width of 50 mm. It is possible to select between Vulkollan and Polyurethane as castor wheel material. Depending on the application, the load on the wheel suspension is handled differently. 3 different types of BT Castor Link are available, but they all rely on the same basic principle.
-
Page 46
Product details Feature When the truck turns or passes a bump, pressure increases on one castor wheel as a result of compression of the spring. Thanks to the torsion tube, the other spring will compress by an identical amount. Benefit The truck remains stable and will never start to rock and travel like a ‘walking duck’, a classic phenomenon when spring forces do not interact. -
Page 47: Fork Carriage
Product details Fork carriage As far as the fork carriage is concerned, all bushings and axles, both classic prob- lem sources, have been improved. This chapter describes these parts together with the forks and fork wheels. Two fork carriages are used, narrow and standard. Feature Narrow fork carriage with 156 mm wide forks.
-
Page 48
Product details Axles and bushings Because bushings and axles are highly vulnerable parts, new high-quality materials have been developed for the LWE and SWE truck series. The results from truck life cycle tests have been very positive. Feature The bushings are made from Teflon-coated composite material. Benefit Teflon-coated composite bushings offer extended length of service and do not re- quire lubrication. -
Page 49: Battery Compartments, Batteries And Chargers
Product details Battery compartments, batteries and chargers When selecting the battery, these aspects should be considered: ● Physical limitations of the battery compartment – information on battery com- partment sizes is available in the Technical information chapter. ● Minimum and maximum weight –- these weights are indicated in the Technical information chapter.
-
Page 50
Product details Feature It is possible to select a desired battery compartment size. On the larger models, battery replacement to the side is available as an option. Benefit The truck can be optimised for the intended application. For higher intensive ap- plications, lateral battery replacement is a recommended option. -
Page 51
Product details Battery connector and charging To charge the battery, disconnect the battery connector and connect it to the battery charger. The battery connector should also be disconnected in the following situa- tions to cut the power supply: ● In the event of an accident. ●… -
Page 52
Product details Feature Different types of chargers provide different characteristics: ● Conventional, unregulated chargers are sensitive to line voltage fluctuations. As a result, the charging duration can vary, however, these chargers are cost-effec- tive. ● HF chargers are not as sensitive to fluctuations in the line voltage, and they are able to carefully control the charging process and as a result the charging dura- tion. -
Page 53: Technical Information
Technical information Technical information Dimensions and performance figures x measurement The x measurement is the distance back●of●fork●to●the●fork●wheel●centre. For trucks with bogie wheels, it is measured from back●of●fork●to●fork●bogie-wheel● centre. Usually this measurement is available in the Product information. l measurement The l measurement is the Total●fork●length. measurement The l measurement is the Truck●length●including●back●of●fork.
-
Page 54
Technical information u measurement The u measurement is the distance between fork● tip● and● the● wheel-fork● pivot● point. T measurement The measurement from●back●of●forks●to●the●wheel●fork●pivot●point is called the T measurement. The T measurement can be calculated with the formula: T = l -u As an example the u and T measurements are important for long side handling of pallets. -
Page 55
Technical information Standard fork length tables LWE140/160 X down, Fl-u+119 X up, Fl-u+64 1000 1070 1120 1150 1200 1220 1019 1370 1085 1204 1149 1450 1165 1284 1229 1520 1235 1354 1299 LWE180/200/250 X down, Fl-u+116 X up, Fl-u+59 1000 1050 1070 1100… -
Page 56
Technical information e, b and b measurements LWE140 LWE160 LWE180 LWE200 LWE250 measurement, height of fork in lowered position measurement, height of fork in raised position. e measurement, fork width measurement, width over forks The b measurement is referred to as the width●over●forks. This measurement must suit the pallets to be handled by the truck. -
Page 57: Aisle Width Requirement
Technical information , turning radius The turning radius is the necessary Distance●to●turn●the●truck●around●a●virtual● point●referred●to●as●the●turning●centre with forks raised. The product informa- tion provides Wa measurements for all LWE truck versions. – Aisle width requirement The aisle width requirement can be described as the space required by the truck to pick a pallet from a pallet rack, reverse out in the aisle, turn and proceed down the aisle.
-
Page 58: Aisle Width Requirements
Technical information Aisle width requirements Truck Battery comp. Aisle width for pallets: LWE140 small 1420 1842 1000×1200 longside handling small 1420 1892 800×1200 shortside handling Truck Battery comp. Aisle width for pallets: LWE160 small 1420 1842 1000×1200 longside handling small 1420 1892 800×1200 shortside handling…
-
Page 59
Technical information Calculating A according to the standard, LWE range ● The values are from the Product information sheet for LWE200. Standard: A = 1447 + (1200 — 898) + 2×100 = 1949 Length of pallet must be substituted by total fork length Standard: A = 1447+ (1150 — 898) + 2×100 = 1899… -
Page 60: Pallets And Pallet Sizes
Technical information Pallets and pallet sizes 1200 Euro pallet 382,5 382,5 ● Outer dimensions: 800 × 1200 mm ● Pallet height: 144 mm 227,5 227,5 ● Height, fork entries: 100 all four sides ● Corners: 45° ● Pallet weight: approximately 27 kg ●…
-
Page 61: Choosing The Optimal Fork Specification
Technical information Choosing the optimal fork specification When forks suited for a pallet or a specific roll container, these items should be considered: ● The b measurement must suit the pallet /roll container to enable positioning of the forks between the pallet legs or between the wheels of the roll container. Example: With Width over Forks 450 mm and Fork Width 180 mm, only 90 mm remains between the forks and the truck will not be able to handle Euro pallets or Chep pallets.
-
Page 62: Battery Weights
Technical information Battery weights LWE140 Batt. compartment Min. batt. weight kg Max. batt. weight kg Capacity Ah Volt V Size L*W*H mm Small 651 x 150 x 570 LWE160 Batt. compartment Min. batt. weight kg Max. batt. weight kg Capacity Ah Volt V Size L*W*H mm Small 651 x 150 x 570 Medium…
-
Page 63: Battery And Charger
Technical information Battery and charger Information on Hawker Evolution GEL batteries Hawker Evolution GEL batteries is the only type of valve-regulated batteries of- fered for the trucks in the LWE series. Please note the following if selecting a bat- tery of this type for the truck: ●…
-
Page 64
Technical information Product guide – BT Levio W-series… -
Page 65: Options
Options Options To adapt the truck to customer preferences, a number of options are available. Battery change from the side Battery roller bed which enables lateral battery replacement (only for trucks with a large bat- tery compartment). Not available for LWE140, LWE160 and LWE180.
-
Page 66: Battery Change Table
Options Battery change table To facilitate battery change from the side, an exter- nal battery change table is also available. The height from the floor to the top of the rollers is adjustable. The battery change table measurments are 834 x 912 mm.
-
Page 67: Built-In Charger
Options Built-in charger When connected to 230 V, the charger has a capacity of 30 A.It is self-adjusting and can be used for voltages between 90 V and 255 V AC, 45 to 400 Hz. For voltages under 200 V, the output current will be reduced. Freely ventilated batteries up to 320 Ah and valve regulated batteries from 134 to 213 Ah can be charged.
-
Page 68: Spacer For Long Side Pallet Handling
Options Feature Any error codes generated by the battery charger are displayed on the display. Benefit This simplifies fault diagnosis if required. Feature When the built-in charger is used, it is not possible to charge the battery unless the battery cover is opened since the power cord needs to be pulled out from behind the cover.
-
Page 69: Truck Log Systems
Truck log systems Toyota I-site Toyota I-site is a truck log and fleet management system that provides possibili- ties to monitor truck usage and operator performance. Toyota I-site is offered a monthly fee basis where we provide a continual process of analysis and consul- tancy to customers and give them access to our knowledge and skills to help us build customer relations.
-
Page 70
Options If the shock sensor is included in the system, information about collisions and im- pacts can be viewed. By monitoring truck usage and operator performance, customers can improve op- erations and reduce cost. Access to different levels of information can be set for different users/functions in the company. -
Page 71: Integrated E-Bar With Optional Accessories
Options Integrated E-bar with optional accessories All trucks in the LWE series, except for those with small battery compartment, can be fitted with an optional E-bar. This is BT’s standard solution for mounting a writing holder, plastic film holder, computer terminal, PC, scanner or other electronic equipment required onboard the truck.
-
Page 72: Turtle Button
Options Turtle button The turtle button allows temporary reduction of speed. The default setting for speed reduction is – 50 %, i.e. the travel speed will be reduced to 3 km/h. If necessary, this can be reprogrammed by a service technician. Feature When the turtle button is pressed once, the truck enters the turtle mode and travels at reduced speed.
-
Page 73: Operator Platform
Options Operator platform An operator platform is a useful option if the travel distances are a bit longer and the operator wants to have the comfort of a stand-on platform. The LWE series offers two different platform types, one with a rubber mat and automatic fold-up and a cold-store version with a checkered plate and also automatic fold-up.
-
Page 74
Options Feature The cold-store version of the platform uses a checkered plate. Benefit The checkered plate assures good friction even in cold stores and also in foodstuff applications where operators often wear wet or slippery shoes. Feature The platform is secured to a frame with rounded corners. Benefit The frame offers numerous benefits: ●… -
Page 75: Load Support
Options Load support The optional load support is attached to the back of the forks and is available on all LWE trucks. Feature The load support has a height of 1500 mm (from the top of the forks). Benefit This added support protects the operator and goods.
-
Page 76: Rubber Border
Options Rubber border A rubber border is available for all BT Levio W-series models. The trucks can be ordered with a rubber border instead of the standard steel border to allow high gradient ramp handling ability. The rubber border is especially suited for applications with high thresholds, curbs and ramps with high gradients.
-
Page 77: Appendix
Appendix Appendix Environmental work within BT The BT trucks are produced at manufacturing sites where environmental issues are in focus. Waste management and reduction of hazardous chemicals used in production are natural parts of the everyday environmental work. We have been ISO 14001 certified since 1997, and in our continuous environmental work we put effort into reducing energy consumption on all levels, while we work with preven- tive actions to reduce pollution risks and the risk of biological danger.
-
Page 78: Focus On Quality Within Bt
Appendix Focus on quality within BT The Toyota Way is based on the Guiding Principles at Toyota. Its five core values express the beliefs and values used in the daily work: Challenge To maintain a long-term vision and meet all challenges with the courage and crea- tivity needed to realise that vision.
-
Page 79
Appendix Products and components are tested and evaluated throughout the development process, both in lab environments and field tests. As a complement to calculations, structural tests as well as life time tests are performed. Apart from the functional testing and control made on all products before delivery, product quality is continuously monitored during manufacturing through welding audits on components and product audits on completed trucks. -
Page 80: Certificates
Appendix Certificates Product guide – BT Levio W-series…
-
Page 81
Appendix Product guide – BT Levio W-series…
Все ошибки TOYOTA 4RUNNER, ALLEX, ALLION, ALPHARD, ALTEZZA, ARISTO, AURION, AURIS, AVALON, AVENSIS, AYGO, BB, BELTA, BLADE, BREVIS,CALDINA, CAMI, CAMRY, CELICA, CELSIOR, CENTURY, COROLLA, ECHO, ESTIMA, FJ CRUISER, FORTUNER, FUNCARGO, GT86, HARRIER, HIACE, HIGHLANDER, HILUX, INNOVA, IPSUM, iQ, ISIS, IST, KLUGER HYBRID, KLUGER V, LAND CRUISER, LAND CRUISER PRADO, MARK, MARK X, MATRIX, MR 2, NADIA, NOAH, OPA, PASSO, PLATZ, PREMIO, PREVIA, PRIUS, PROBOX, PROGRES, RACTIS, RAUM, RAV4, RUSH, SAI, SEQUOIA, SIENNA, SIENTA, SOLARA, TACOMA, TUNDRA, URBAN CRUISER, VANGUARD, VELLFIRE, VENZA, VERSO, VITZ, VOLTZ, VOXY, WILL CYPHA, WILL VS, WINDOM, WISH, YARIS.

Ошибки Toyota по протоколу OBDI. Самодиагностика.
Бензиновые двигатели
12 — Датчик положения коленчатого вала (P0335)
13 — Датчик положения коленчатого вала (P0335, P1335)
14 — Система зажигания, катушка №1 (P1300) и №4 (P1315)
15 — Система зажигания, катушка №2 (P1305) и №3 (P1310)
16 — Система управления АКПП
18 — Система VVT-i — фазы (P1346)
19 — Датчик положения педали акселератора (P1120)
19 — Датчик положения педали акселератора (P1121)
21 — Кислородный датчик (P0135)
22 — Датчик температуры охлаждающей жидкости (P0115)
24 — Датчик температуры воздуха на впуске (P0110)
25 — Кислородный датчик — сигнал бедной смеси (P0171)
27 — Кислородный датчик №2
31 — Датчик абсолютного давления (P0105, P0106)
34 — Система турбонаддува
35 — Датчик давления турбонаддува
36 — Датчик CPS (P1105)
39 — Система VVT-i (P1656)
41 — Датчик положения дроссельной заслонки (P0120, P0121)
42 — Датчик скорости автомобиля (P0500)
43 — Сигнал стартера
47 — Датчик положения дополнительной дроссельной заслонки
49 — Датчик давления топлива (D-4) (P0190, P0191)
51 — Состояние выключателей
52 — Датчик детонации (P0325)
53 — Сигнал детонации
55 — Датчик детонации №2
58 — Привод SCV (D-4) (P1415, P1416, P1653)
59 — Сигнал VVT-i (P1349)
71 — Система EGR (P0401, P0403)
78 — ТНВД (D-4)
89 — Привод ETCS (P1125, P1126, P1127, P1128, P1129, P1633)
92 — Форсунка холодного пуска (D-4) (P1210)
97 — Форсунки (D-4) (P1215)
Дизельные двигатели
12 – Датчик положения коленчатого вала
13 – Датчик частоты вращения
14 – Клапан регулировки угла опережения впрыска
15 – Сервопривод дроссельной заслонки
17 – Сигнал блока управления
18 – Электромагнитный перепускной клапан
19 – Датчик положения педали акселератора
22 – Датчик температуры охлаждающей жидкости
24 – Датчик температуры воздуха на впуске
32 – Корректирующие резисторы
35 – Датчик давления наддува
39 – Датчик температуры топлива
42 – Датчик скорости автомобиля
96 – Датчик положения клапана EGR
АКПП
11 – Норма
37 – Датчик частоты вращения входного вала АКПП (Р1705)
38 – Датчик температуры рабочей жидкости АКПП
42 – Датчик скорости (или датчик частоты вращения выходного вала) (Р0500)
44 – Датчик скорости (или датчик частоты вращения заднего выходного вала)
46 – Соленоид управления давлением гидроаккумулятора (Р1765)
61 – Датчик скорости (или датчик частоты вращения переднего выходного вала)
62 – Соленоид №1 (Р0753)
63 – Соленоид №2 (Р0758)
64 – Соленоид муфты блокировки гидротрансформатора (Р0773)
67 – Датчик частоты вращения входного вала АКПП
68 – Соленоид управления муфтой блокировки гидротрансформатора
73 – Соленоид муфты блокировки межосевого дифференциала
ABS
11 – Обрыв цепи реле электромагнитного клапана
12 – Короткое замыкание в цепи реле э/м клапана
13 – Обрыв в цепи реле электронасоса
14 – Короткое замыкание в цепи реле электронасоса
21 – Обрыв или короткое замыкание в э/м клапане переднего правого колеса
22 – Обрыв или короткое замыкание в э/м клапане переднего левого колеса
23 – Обрыв или короткое замыкание в э/м клапане заднего правого (левого) колеса
24 – Обрыв или короткое замыкание в э/м клапане заднего левого (правого) колеса
31 – Неисправность датчика частоты вращения переднего правого колеса
32 – Неисправность датчика частоты вращения переднего левого колеса
33 – Неисправность датчика частоты вращения заднего правого колеса
34 – Неисправность датчика частоты вращения заднего левого колеса
41 – Слишком высокое или слишком низкое напряжение аккумуляторной батареи
43 – Неисправность в цепи датчика замедления
44 – Обрыв или короткое замыкание в цепи датчика замедления
49 – Обрыв в цепи выключателя стоп-сигналов
51 – Короткое замыкание или обрыв цепи питания электронасоса
71 – Низкий уровень сигнала от датчика частоты вращения переднего правого колеса
72 – Низкий уровень сигнала от датчика частоты вращения переднего левого колеса
73 – Низкий уровень сигнала от датчика частоты вращения заднего правого колеса
74 – Низкий уровень сигнала от датчика частоты вращения заднего левого колеса
75 – Неправильное изменение сигнала от датчика частоты вращения переднего правого колеса
76 – Неправильное изменение сигнала от датчика частоты вращения переднего левого колеса
77 – Неправильное изменение сигнала от датчика частоты вращения заднего правого колеса
78 – Неправильное изменение сигнала от датчика частоты вращения заднего левого колеса
79 – Неисправность датчика замедления
98 – Датчик разрежения в вакуумном усилителе тормозов (C1200) колеса
Системы безопасности (SRS)
11 – Воспламенитель ПБ водителя (замыкание на массу)
12 – Воспламенитель ПБ водителя (замыкание на питание)
13 – Воспламенитель ПБ водителя (замыкание в цепи)
14 – Воспламенитель ПБ водителя (разрыв в цепи)
15 – Передний правый датчик SRS (замыкание или разрыв в цепи)
15 – Передний правый датчик SRS (замыкание на массу или питание)
16 – Передний левый датчик SRS (замыкание или разрыв в цепи)
16 – Передний левый датчик SRS (замыкание на массу или питание)
31 – Неисправность блока управления SRS
51 – Воспламенитель ПБ пассажира (замыкание на массу)
52 – Воспламенитель ПБ пассажира (замыкание на питание)
53 – Воспламенитель ПБ пассажира (замыкание в цепи)
54 – Воспламенитель ПБ пассажира (разрыв в цепи)
61 – Воспламенитель преднатяжителя ремня водителя (замыкание на массу)
62 – Воспламенитель преднатяжителя ремня водителя (замыкание на питание)
63 – Воспламенитель преднатяжителя ремня водителя (замыкание в цепи)
64 – Воспламенитель преднатяжителя ремня водителя (разрыв в цепи)
71 – Воспламенитель преднатяжителя ремня пассажира (замыкание на массу)
72 – Воспламенитель преднатяжителя ремня пассажира (замыкание на питание)
73 – Воспламенитель преднатяжителя ремня пассажира (замыкание в цепи)
74 – Воспламенитель преднатяжителя ремня пассажира (разрыв в цепи)
Полный привод (4WS)
11 – Электронный блок управления 4WS
12 – Неисправность главного электродвигателя заднего рулевого механизма
13 – Неисправность привода управления рулевым механизмом
21 – Короткое замыкание в системе главного электродвигателя
22 – Разрыв цепи в системе главного электродвигателя
23 – Блокировка главного электродвигателя
24 – Неисправность в работе главного электродвигателя
31 – Разрыв в системе электродвигателя заднего хода
32 – Неисправность в работе электродвигателя заднего хода
41 – Неисправность датчика частоты вращения левого переднего колеса
42 – Неисправность датчика системы 4WS
43 – Неверная работа датчика системы 4WS
Ошибки Toyota по протоколу OBDII
Топливная система и воздухоподача
P0000-P0099, P0100-P0199, P0200-P0299
P0010 – Неисправность в электрической цепи привода системы изменения фаз газораспределения, впуск/левый/передний, банк 1
P0011 – Положение распределительного вала, впуск/левый/передний, банк 1 — слишком ранний угол открывания клапанов / нарушение функционирования системы
P0012 – Положение распределительного вала, впуск/левый/передний, банк 1 — слишком поздний угол открывания клапанов
P0015 – Привод системы изменения фаз газораспределения, выпуск/правый/задний, банк 1 — слишком поздний угол открывания
P0016 – Положение коленчатого и распределительного валов, банк 1, датчик А — нет соответствия
P0017 – Положение коленчатого и распределительного валов, банк 1, датчик В — корреляция
P0018 – Положение коленчатого и распределительного валов, банк 2, датчик А — корреляция
P0030 – Неисправность в электрической цепи подогреваемого кислородного датчика 1, банк 1, управление нагревателем
P0031 – Низкое напряжение в электрической сети подогреваемого кислородного датчика 1, банк 1, управление нагревателем
P0032 – Высокое напряжение в электрической сети подогреваемого кислородного датчика 1, банк 1, управление нагревателем
P0036 – Неисправность в электрической цепи подогреваемого кислородного датчика 2, банк 1, управление нагревателем
P0037 – Низкое напряжение в электрической цепи подогреваемого кислородного датчика 2, банк 1, управление нагревателем
P0038 – Высокое напряжение в электрической цепи подогреваемого кислородного датчика 2, банк 1, управление нагревателем
P0045 – Электромагнитный клапан управления давлением турбонаддува/ клапан управления давлением наддува приводного нагнетателя — обрыв цепи
P0046 – Электромагнитный клапан управления давлением турбонаддува / давлением наддува приводного нагнетателя — диапазон/функционирование
P0047 – Электромагнитный клапан управления давлением турбонаддува / давлением наддува приводного нагнетателя — низкий уровень сигнала
P0048 – Электромагнитный клапан управления давлением турбонаддува / давлением наддува приводного нагнетателя — высокий уровень сигнала
P004B – Управление “В” давлением наддува турбокомпрессора/приводного нагнетателя — диапазон/функционирование
P004C – Управление “В” давлением наддува турбокомпрессора/приводного нагнетателя — низкий уровень сигнала
P004D – Управление “В” давлением наддува турбокомпрессора/приводного нагнетателя — высокий уровень сигнала
P0050 – Неисправность в электрической цепи подогреваемого кислородного датчика 1, банк 2, управление нагревателем
P0051 – Низкий уровень сигнала подогреваемого кислородного датчика 1, банк 2, управление нагревателем
P0052 – Высокий уровень сигнала подогреваемого кислородного датчика 1, банк 2, управление нагревателем
P0056 – Неисправность в электрической цепи подогреваемого кислородного датчика 2, банк 2, управление нагревателем
P0057 – Низкий уровень сигнала подогреваемого кислородного датчика 2, банк 2, управление нагревателем
P0058 – Высокий уровень сигнала подогреваемого кислородного датчика 2, банк 2, управление нагревателем
P0093 – Значительная утечка в топливной системе
P00B0 -Управление “В” давлением наддува турбокомпрессора/приводного нагнетателя — характеристики блока управления
P0100 – Неисправность в электрической цепи датчик расхода воздуха (массового — MAF) / (объемного — VAF)
P0101 – Датчик расхода воздуха (MAF) / (VAF) — диапазон/функционирование
P0102 – Низкий уровень входного сигнала датчика расхода воздуха (MAF) / (VAF)
P0103 – Высокий уровень входного сигнала датчика расхода воздуха (MAF) / (VAF)
P0104 – Ненадежный контакт в электрической цепи датчика расхода воздуха (MAF) / (VAF)
P0105 – Неисправность в электрической цепи датчика абсолютного давления во впускном коллекторе (МАР) / датчика атмосферного давления
P0110 – Неисправность в электрической цепи датчика температуры воздуха на впуске
P0111 – Датчик температуры воздуха на впуске — диапазон/функционирование
P0112 – Низкий уровень сигнала датчика температуры воздуха на впуске
P0113 – Высокий уровень сигнала датчика температуры воздуха на впуске
P0114 – Датчик температуры воздуха на впуске — ненадежный контакт электрической цепи
P0115 – Неисправность в электрической цепи датчика температуры охлаждающей жидкости
P0116 – Датчик температуры охлаждающей жидкости — диапазон/функционирование
P0117 – Низкий уровень сигнала датчика температуры охлаждающей жидкости
P0118 – Высокий уровень сигнала датчика температуры охлаждающей жидкости
P011B – Температура охлаждающей жидкости/температура воздуха на впуске — корреляция
P0120 – Неисправность в электрической цепи датчика положения дроссельной заслонки / датчика положения педали акселератора
P0121 – Датчик положения дроссельной заслонки / датчик положения педали акселератора — диапазон/функционирование
P0122 – Низкий уровень сигнала датчика положения дроссельной заслонки / датчика положения педали акселератора
P0123 – Высокий уровень сигнала датчика положения дроссельной заслонки / датчика положения педали акселератора
P0124 – Датчик положения дроссельной заслонки / датчик положения педали акселератора — ненадежный контакт электрической цепи
P0125 – Температура охлаждающей жидкости недостаточна для управления топливоподачей с обратной связью
P0130 – Неисправность в электрической цепи кислородного датчика 1, банк 1
P0131 – Низкое напряжение в электрической цепи кислородного датчика 1, банк 1
P0132 – Высокое напряжение в электрической цепи кислородного датчика 1, банк 1
P0133 – Малое быстродействие кислородного датчика 1, банк 1
P0134 – Нет отклика от кислородного датчика 1, банк 1
P0135 – Неисправность в электрической цепи подогреваемого кислородного датчика 1, банк 1, управление нагревателем
P0136 – Неисправность в электрической цепи кислородного датчика 2, банк 1
P0137 – Низкое напряжение в электрической цепи кислородного датчика 2, банк 1
P0138 – Высокое напряжение в электрической цепи кислородного датчика 2, банк 1
P0139 – Малое быстродействие кислородного датчика 2, банк 1
P0140 – Нет отклика от кислородного датчика 2, банк 1
P0141 – Неисправность в электрической цепи подогреваемого кислородного датчика 2, банк 1, управление нагревателем
P0155 – Неисправность в электрической цепи кислородного датчика 1, банк 2, управление нагревателем
P0156 – Неисправность в электрической цепи кислородного датчика 2, банк 2
P0157 – Низкое напряжение в электрической цепи кислородного датчика 2, банк 2
P0158 – Высокое напряжение в электрической цепи кислородного датчика 2, банк 2
P0159 – Малое быстродействие кислородного датчика 2, банк 2
P0160 – Нет отклика от кислородного датчика 2, банк 2
P0161 – Неисправность в электрической цепи подогреваемого кислородного датчика 2, банк 2, управление нагревателем
P0170 – Топливный баланс, банк 1 — неисправность
P0171 – Слишком бедная топливовоздушная смесь, банк 1
P0172 – Слишком богатая топливовоздушная смесь, банк 1
P0173 – Топливный баланс, банк 2 — неисправность
P0174 – Слишком бедная топливовоздушная смесь, банк 2
P0175 – Слишком богатая топливовоздушная смесь, банк 2
P0190 – Неисправность в электрической цепи датчика давления в топливной рейке
P0191 – Датчик давления в топливной рейке — диапазон/функционирование
P0192 – Низкий уровень сигнала в электрической цепи датчика давления в топливной рейке
P0193 – Высокий уровень сигнала в электрической цепи датчика давления в топливной рейке
P0200 – Неисправность в электрической цепи форсунки
P0201 – Неисправность в электрической цепи форсунки № 1
P0202 – Неисправность в электрической цепи форсунки № 2
P0203 – Неисправность в электрической цепи форсунки № 3
P0204 – Неисправность в электрической цепи форсунки № 4
P0205 – Неисправность в электрической цепи форсунки № 5
P0206 – Неисправность в электрической цепи форсунки № 6
P0207 – Неисправность в электрической цепи форсунки № 7
P0208 – Неисправность в электрической цепи форсунки № 8
P0209 – Неисправность в электрической цепи форсунки № 9
P0210 – Неисправность в электрической цепи форсунки № 10
P0211 -Неисправность в электрической цепи форсунки № 11
P0212 – Неисправность в электрической цепи форсунки № 12
Система зажигания
P0300-P0399
P0300 – Случайные / множественные пропуски зажигания (воспламенения)
P0301 – Пропуски зажигания (воспламенения) в цилиндре № 1
P0302 – Пропуски зажигания (воспламенения) в цилиндре № 2
P0303 – Пропуски зажигания (воспламенения) в цилиндре № 3
P0304 – Пропуски зажигания (воспламенения) в цилиндре № 4
P0305 – Пропуски зажигания (воспламенения) в цилиндре № 5
P0306 – Пропуски зажигания (воспламенения) в цилиндре № 6
P0307 – Пропуски зажигания (воспламенения) в цилиндре № 7
P0308 – Пропуски зажигания (воспламенения) в цилиндре № 8
P0309 – Пропуски зажигания (воспламенения) в цилиндре № 9
P0310 – Пропуски зажигания (воспламенения) в цилиндре № 10
P0311 – Пропуски зажигания (воспламенения) в цилиндре № 11
P0312 – Пропуски зажигания (воспламенения) в цилиндре № 12
P0325 – Неисправность в электрической цепи датчика детонации 1, банк 1
P0326 – Датчик детонации 1, банк 1 — диапазон/функционирование
P0327 – Низкий уровень сигнала в электрической цепи датчика детонации 1, банк 1
P0328 – Высокий уровень сигнала в электрической цепи датчика детонации 1, банк 1
P0329 – Датчик детонации 1, банк 1 — ненадежный контакт электрической цепи
P0330 – Неисправность в электрической цепи датчика детонации 2, банк 2
P0331 – Датчик детонации 2, банк 2 — диапазон/функционирование
P0332 – Низкий уровень сигнала в электрической цепи датчика детонации 2, банк 2
P0333 – Высокий уровень сигнала в электрической цепи датчика детонации 2, банк 2
P0334 – Датчик детонации 2, банк 2 — ненадежный контакт электрической цепи
P0335 – Неисправность в электрической цепи датчика положения коленчатого вала
P0336 – Датчик положения коленчатого вала — диапазон/функционирование
P0337 – Датчик положения коленчатого вала — низкий уровень сигнала
P0338 – Датчик положения коленчатого вала — высокий уровень сигнала
P0339 – Датчик положения коленчатого вала — ненадежный контакт электрической цепи
P0340 – Неисправность в электрической цепи датчика положения распределительного вала
P0341 – Датчик положения распределительного вала — диапазон/функционирование
P0342 – Датчик положения распределительного вала — низкий уровень сигнала
P0343 – Датчик положения распределительного вала — высокий уровень входного сигнала
P0344 – Датчик положения распределительного вала — ненадежный контакт электрической цепи
P0345 – Неисправность в электрической цепи датчика положения распределительного вала “A”, банк 2
P0346 – Датчик положения распределительного вала “A”, банк 2 — диапазон/функционирование
P0347 – Датчик положения распределительного вала “A”, банк 2 — низкий уровень сигнала
P0348 – Датчик положения распределительного вала “A”, банк 2 — высокий уровень сигнала
P0349 – Датчик положения распределительного вала “A”, банк 2 — ненадежный контакт электрической цепи
P0350 – Катушка зажигания, первичная/вторичная обмотки — неисправность электрической цепи
P0351 – Катушка зажигания “A”, первичная/вторичная обмотки — неисправность электрической цепи
P0352 – Катушка зажигания “В”, первичная/вторичная обмотки — неисправность электрической цепи
P0353 – Катушка зажигания “С”, первичная/вторичная обмотки — неисправность электрической цепи
P0354 – Катушка зажигания “D”, первичная/вторичная обмотки — неисправность электрической цепи
P0355 – Катушка зажигания “Е”, первичная/вторичная обмотки — неисправность электрической цепи
P0356 – Катушка зажигания “F”, первичная/вторичная обмотки — неисправность электрической цепи
P0357 – Катушка зажигания “G”, первичная/вторичная обмотки — неисправность электрической цепи
P0358 – Катушка зажигания “H”, первичная/вторичная обмотки — неисправность электрической цепи
P0359 – Катушка зажигания “I”, первичная/вторичная обмотки — неисправность электрической цепи
P0360 – Катушка зажигания “J”, первичная/вторичная обмотки — неисправность электрической цепи
P0361 – Катушка зажигания “K”, первичная/вторичная обмотки — неисправность электрической цепи
P0362 – Катушка зажигания “L”, первичная/вторичная обмотки — неисправность электрической цепи
P0368 – Датчик “В” положения распределительного вала, банк 1 — высокий уровень сигнала
P0393 – Датчик “В” положения распределительного вала, банк 2 — высокий уровень входного сигнала
Контроль выбросов
P0400-P0499
P0400 – Система рециркуляции отработавших газов (EGR) — неисправность каналов системы
P0401 – Система рециркуляции отработавших газов (EGR) — недостаточный уровень рециркуляции
P0405 – Датчик положения клапана А системы рециркуляции ОГ (EGR) — низкий уровень сигнала
P0418 – Реле насоса А подачи воздуха на выпуск — неисправность электрической цепи
P0420 – Каталитический нейтрализатор, банк 1 — эффективность ниже требуемой
P0430 – Каталитический нейтрализатор, банк 2 — эффективность ниже требуемой
P0441 – Система улавливания паров топлива — некорректный расход
P0442 – Система улавливания паров топлива — незначительная утечка
P0443 – Электромагнитный клапан аккумулятора паров топлива — неисправность электрической цепи
P0446 – Система улавливания паров топлива, управление продувкой — неисправность электрической цепи
P0456 – Система улавливания паров топлива — крайне незначительная утечка
Контроль скорости и холостого хода
P0500-P0599
P0500 – Неисправность в электрической цепи датчика скорости автомобиля
P0504 – Выключатель А/В стоп-сигналов (датчик положения педали тормоза) — корреляция
P0505 – Система управления частотой вращения холостого хода — неисправность
P0556 – Датчик давления в системе усилителя тормозной системы — диапазон/функционирование
P0560 – Напряжение системы (бортовой сети) — неисправность
Электронный блок управления (ЭБУ) и его подсистемы
P0600-P0699
P0606 – Электронный блок управления двигателем (ECM) / блок управления силовым агрегатом (PCM) — неисправность процессора
Трансмиссия
P0700-P0799, P0800-P0899, P0900-P0999
P0703 – Выключатель стоп-сигналов “B” — неисправность электрической цепи
P0705 – Датчик положения селектора АКПП, входной сигнал PRNDL — неисправность электрической цепи
P0715 – Датчик частоты вращения входного вала АКПП (турбины гидротрансформатора) — неисправность электрической цепи
P0724 – Выключатель стоп-сигналов “B” — высокий уровень сигнала
P0741 – Электромагнитный клапан муфты блокировки гидротрансформатора — функционирование или «залипание» в закрытом состоянии
P0746 – Электромагнитный клапан управления давлением рабочей жидкости КПП — функционирование или «залипание» в закрытом состоянии
P0748 – Электромагнитный клапан управления давлением рабочей жидкости КПП — электрическая неисправность
P0753 – Электромагнитный клапан “А” переключения передач — электрическая неисправность
P0758 – Электромагнитный клапан “В” переключения передач — электрическая неисправность
P0778 – Электромагнитный клапан “В” управления давлением — электрическая неисправность
P0793 – Датчик частоты вращения промежуточного вала КПП — нет сигнала
P0810 – Ошибка в управлении сцеплением (муфтой)
P0812 – Передача заднего хода — неисправность входной цепи
P0820 – Датчик положения X-Y рычага переключения — неисправность электрической цепи
P0900 – Привод сцепления — обрыв цепи
P0907 – Цепь выбора диапазона коробки передач — высокое напряжение
P0909 – Ошибка выбора диапазона коробки передач
P0910 – Привод выбора диапазона коробки передач — обрыв цепи
P0915 – Цепь определения включенной передачи — диапазон/функционирование
P0917 – Цепь определения включенной передачи — высокое напряжение цепи
P0919 – Контроль включенной передачи — ошибка
P0974 – Электромагнитный клапан “А” переключения передач — высокий уровень сигнала
P0999 – Электромагнитный клапан “F” переключения передач — высокий уровень сигнала
Другие ошибки
P1047 – Ошибка параметра настройки блока управления Valvematic / неисправность цепи питания ряда 1
P1049 – Неисправность внутренней цепи блока управления Valvematic ряда 1
P1100 – Неисправность в электрической цепи датчика атмосферного давления
P1105 – Неисправность в электрической цепи датчика давления в камере сгорания
P2002 – Сажевый фильтр, банк 1 — эффективность ниже требуемой
P2006 – Привод изменения геометрии впускного коллектора, банк 1 — привод завис в закрытом положении
P2008 – Привод системы изменения геометрии впускного коллектора, банк 1 — обрыв цепи
P2103 – Электродвигатель привода дроссельной заслонки — высокий уровень сигнала
P2109 – Датчик А положения педали акселератора — минимальное ограничение
P2111 – Система управления приводом дроссельной заслонки — заедание привода в открытом положении
P2112 – Система управления приводом дроссельной заслонки — заедание привода в закрытом положении
P2118 – Привод дроссельной заслонки, ток электродвигателя — диапазон/функционирование
P2121 – Датчик положения педали акселератора/выключатель D — диапазон/функционирование
P2123 – Датчик положения педали акселератора/выключатель D — высокий уровень входного сигнала
P2138 – Датчик положения педали акселератора/выключатель D/Е — корреляция напряжения
P2146 – Форсунки — группа A, напряжение питания — обрыв цепи
P2149 – Форсунки — группа B, напряжение питания — обрыв цепи
P2195 – Подогреваемый кислородный датчик 1, банк 1 — сигнал постоянно бедной смеси
P2196 – Подогреваемый кислородный датчик 1, банк 1 — сигнал постоянно богатой смеси
P2197 – Подогреваемый кислородный датчик 1, банк 2 — сигнал постоянно бедной смеси
P2198 – Подогреваемый кислородный датчик 1, банк 2 — сигнал постоянно богатой смеси
P2237 – Подогреваемый кислородный датчик 1, банк 1, управление током (+) — обрыв цепи
P2238 – Подогреваемый кислородный датчик 1, банк 1, управление током (+) — низкий уровень
P2240 – Подогреваемый кислородный датчик 1, банк 2, управление током (+) — обрыв цепи
P2432 – Система подачи воздуха на выпуск, датчик расхода/давления, банк 1 — низкий уровень сигнала
P2440 – Переключающий электромагнитный клапан подачи воздуха на выпуск, банк 1 — заедание клапана в открытом положении
P2241 – Переключающий электромагнитный клапан подачи воздуха на выпуск, банк 1 — заедание клапана в закрытом положении
P2442 – Переключающий электромагнитный клапан подачи воздуха на выпуск, банк 2 — заедание клапана в открытом положении
P2463 – Сажевый фильтр (DPF) — засорение DPF
P2588 – Датчик 5 температуры отработавших газов, банк 2 — диапазон/функционирование
P2646 – Привод коромысла A, банк 1 — проблемы функционирования или заедание привода в закрытом положении
P2649 – Привод коромысла А, банк 1 — высокий уровень сигнала
P264A – Датчик А положения привода коромысла, банк 1 – неисправность электрической цепи
P2714 – Электромагнитный клапан D управления давлением рабочей жидкости КПП – функционирование или заедание в закрытом положении
P2716 – Электромагнитный клапан D управления давлением рабочей жидкости КПП – электрическая неисправность
P2757 – Электромагнитный клапан управления давлением муфты блокировки гидротрансформатора – функционирование или заедание в закрытом положении
P2759 – Электромагнитный клапан управления давлением муфты блокировки гидротрансформатора – электрическая неисправность
P2763 – Электромагнитный клапан управления давлением муфты блокировки гидротрансформатора – высокий уровень сигнала
P2770 – Муфта гидротрансформатора – высокий уровень сигнала
P2799 – Управление дополнительным насосом рабочей жидкости КПП – высокий уровень сигнала
P2A00 – Подогреваемый кислородный датчик 1, банк 1 – проблемы диапазона/функционирования
P3000 – Неисправность высоковольтной батареи
P3100 – Неисправность блока управления высоковольтной батареи
Bt Industries RRE160:
BT REFLEX RRE 160 error code 3:328
Hi Everyone,
Does anybody know what means error code 3:328 on BT REFLEX RRE 160?
Showing items 1 — 1 of 1 results.
Sort messages by:
3:328 = Short circuit in the ACT, the drive motor or the motor cables.
The truck is braked by the motor brake until it stops.
Check
1.That the motor cables are undamaged and there is no short circuit between them or with B-.
2.The motor windings’ resistance to the motor yoke, there should be no relationship.
3.Test using a new motor controller. If the error persists, the fault is probably an internal motor problem. Replace the motor and refit the old controller.
Both the frequency convertor boxes under the pedals are the same, you can swop there positions & see if the fault then moves to the hydraulic pump motor.
Having trouble using the Discussion Forums? Contact us for help.
Forkliftaction.com accepts no responsibility for forum content and requires forum participants to adhere to the rules. Click here for more information.